SLOS454I January 2005 – July 2016 THS4509
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封裝選項
機(jī)械數(shù)據(jù) (封裝 | 引腳)
- RGT|16
散熱焊盤機(jī)械數(shù)據(jù) (封裝 | 引腳)
- RGT|16
訂購信息
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Over operating free-air temperature range, unless otherwise noted.(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VS– to VS+ | Supply voltage | 6 | V | ||
| VI | Input voltage | ±VS | |||
| VID | Differential input voltage | 4 | V | ||
| IO | Output current(2) | 200 | mA | ||
| Continuous power dissipation | See Dissipation Ratings | ||||
| TJ | Maximum junction temperature | 150 | °C | ||
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 85 | °C | |
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses above these ratings may cause permanent damage. Exposure to absolute maximum conditions for extended periods may degrade device reliability. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those specified is not implied.
(2) The THS4509 incorporates a (QFN) exposed thermal pad on the underside of the chip. This pad acts as a heatsink and must be connected to a thermally dissipative plane for proper power dissipation. Failure to do so may result in exceeding the maximum junction temperature which could permanently damage the device. See TI technical briefs SLMA002 and SLMA004 for more information about using the QFN thermally-enhanced package.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1500 | |||
| Machine model | ±100 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | 3 | 5 | 5.25 | V | |
| Ambient temperature | –40 | 25 | 85 | °C | |
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | THS4509 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGT (VQFN) | |||
| 16 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 49.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 66.9 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 23.7 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 1.7 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 23.7 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 7.1 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
7.5 Electrical Characteristics: VS+ – VS– = 5 V
Test conditions are at VS+ = +2.5 V, VS– = –2.5 V, G = 10 dB, CM = open, VO = 2 VPP, RF = 349 Ω, RL = 200-Ω differential,TA = +25°C, single-ended input, differential output, and input and output referenced to midsupply, unless otherwise noted.
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | TEST LEVEL(1) |
MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC PERFORMANCE | ||||||||
| Small-signal bandwidth | G = 6 dB, VO = 100 mVPP | C | 2 | GHz | ||||
| G = 10 dB, VO = 100 mVPP | 1.9 | GHz | ||||||
| G = 14 dB, VO = 100 mVPP | 600 | MHz | ||||||
| G = 20 dB, VO = 100 mVPP | 275 | MHz | ||||||
| Gain-bandwidth product | G = 20 dB | 3 | GHz | |||||
| Bandwidth for 0.1-dB flatness | G = 10 dB, VO = 2 VPP | 300 | MHz | |||||
| Large-signal bandwidth | G = 10 dB, VO = 2 VPP | 1.5 | GHz | |||||
| Slew rate (differential) | 2-V step | 6600 | V/μs | |||||
| Rise time | 0.5 | ns | ||||||
| Fall time | 0.5 | |||||||
| Settling time to 1% | 2 | |||||||
| Settling time to 0.1% | 10 | |||||||
| 2nd-order harmonic distortion | f = 10 MHz | –104 | dBc | |||||
| f = 50 MHz | –80 | |||||||
| f = 100 MHz | –68 | |||||||
| 3rd-order harmonic distortion | f = 10 MHz | –108 | dBc | |||||
| f = 50 MHz | –92 | |||||||
| f = 100 MHz | –81 | |||||||
| 2nd-order intermodulation distortion | 200-kHz tone spacing, RL = 499 Ω |
fC = 70 MHz | –78 | dBc | ||||
| fC = 140 MHz | –64 | |||||||
| 3rd-order intermodulation distortion | fC = 70 MHz | –95 | ||||||
| fC = 140 MHz | –78 | |||||||
| 2nd-order output intercept point | 200-kHz tone spacing RL = 100 Ω, referenced to 50-Ω output |
fC = 70 MHz | 78 | dBm | ||||
| fC = 140 MHz | 58 | |||||||
| 3rd-order output intercept point | fC = 70 MHz | 43 | ||||||
| fC = 140 MHz | 38 | |||||||
| 1-dB compression point | fC = 70 MHz | 12.2 | dBm | |||||
| fC = 140 MHz | 10.8 | |||||||
| Noise figure | 50-Ω system, 10 MHz | 17.1 | dB | |||||
| Input voltage noise | f > 10 MHz | 1.9 | nV/√Hz | |||||
| Input current noise | f > 10 MHz | 2.2 | pA/√Hz | |||||
| DC PERFORMANCE | ||||||||
| Open-loop voltage gain (AOL) | C | 68 | dB | |||||
| Input offset voltage | TA = +25°C | A | 1 | 4 | mV | |||
| TA = –40°C to +85°C | 1 | 5 | mV | |||||
| Average offset voltage drift | TA = –40°C to +85°C | B | 2.6 | μV/°C | ||||
| Input bias current | TA = +25°C | A | 8 | 15.5 | μA | |||
| TA = –40°C to +85°C | 8 | 18.5 | ||||||
| Average bias current drift | TA = –40°C to +85°C | B | 20 | nA/°C | ||||
| Input offset current | TA = +25°C | A | 1.6 | 3.6 | μA | |||
| TA = –40°C to +85°C | 1.6 | 7 | ||||||
| Average offset current drift | TA = –40°C to +85°C | B | 4 | nA/°C | ||||
| INPUT | ||||||||
| Common-mode input range high | B | 1.4 | V | |||||
| Common-mode input range low | –1.4 | |||||||
| Common-mode rejection ratio | 90 | dB | ||||||
| Differential input impedance | C | 1.3 || 1.8 | MΩ || pF | |||||
| Common-mode input impedance | C | 1.0 || 2.3 | MΩ || pF | |||||
| OUTPUT | ||||||||
| Maximum output voltage high | Each output with 100 Ω to midsupply | TA = +25°C | A | 1.2 | 1.4 | V | ||
| TA = –40°C to +85°C | 1.1 | 1.4 | ||||||
| Minimum output voltage low | TA = +25°C | –1.4 | –1.2 | V | ||||
| TA = –40°C to +85°C | –1.4 | –1.1 | ||||||
| Differential output voltage swing | 4.8 | 5.6 | V | |||||
| TA = –40°C to +85°C | 4.4 | |||||||
| Differential output current drive | RL = 10 Ω | C | 96 | mA | ||||
| Output balance error | VO = 100 mV, f = 1 MHz | –49 | dB | |||||
| Closed-loop output impedance | f = 1 MHz | 0.3 | Ω | |||||
| OUTPUT COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE CONTROL | ||||||||
| Small-signal bandwidth | C | 700 | MHz | |||||
| Slew rate | 110 | V/μs | ||||||
| Gain | 1 | V/V | ||||||
| Output common-mode offset from CM input |
1.25 V < CM < 3.5 V | 5 | mV | |||||
| CM input bias current | 1.25 V < CM < 3.5 V | ±40 | μA | |||||
| CM input voltage high | 1.5 | V | ||||||
| CM input voltage low | –1.5 | |||||||
| CM input impedance | 23 || 1 | kΩ || pF | ||||||
| CM default voltage | 0 | V | ||||||
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||||
| Specified operating voltage | C | 3 | 5 | 5.25 | V | |||
| Maximum quiescent current | TA = +25°C | A | 37.7 | 40.9 | mA | |||
| TA = –40°C to +85°C | 37.7 | 41.9 | ||||||
| Minimum quiescent current | TA = +25°C | 34.5 | 37.7 | mA | ||||
| TA = –40°C to +85°C | 33.5 | 37.7 | ||||||
| Power-supply rejection (±PSRR) | C | 90 | dB | |||||
| POWER-DOWN - Referenced to VS– | ||||||||
| Enable voltage threshold | Assured on above 2.1 V + VS– | C | > 2.1 + VS– | V | ||||
| Disable voltage threshold | Assured off below 0.7 V + VS– | < 0.7 + VS– | V | |||||
| Power-down quiescent current | TA = +25°C | A | 0.65 | 0.9 | mA | |||
| TA = –40°C to +85°C | 0.65 | 1 | ||||||
| Input bias current | PD = VS– | C | 100 | μA | ||||
| Input impedance | 50 || 2 | kΩ || pF | ||||||
| Turnon time delay | Measured to output on | 55 | ns | |||||
| Turnoff time delay | Measured to output off | 10 | μs | |||||
(1) Test levels: (A) 100% tested at +25°C. Over-temperature limits by characterization and simulation. (B) Limits set by characterization and simulation. (C) Typical value only for information.
7.6 Electrical Characteristics: VS+ – VS– = 3 V
Test conditions at VS+ = +1.5 V, VS– = –1.5 V, G = 10 dB, CM = open, VO = 1 VPP, RF = 349 Ω, RL = 200-Ω differential,TA = +25°C, single-ended input, differential output, and input and output referenced to midsupply, unless otherwise noted.
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | TEST LEVEL(1) |
MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC PERFORMANCE | ||||||||
| Small-signal bandwidth | G = 6 dB, VO = 100 mVPP | C | 1.9 | GHz | ||||
| G = 10 dB, VO = 100 mVPP | 1.6 | GHz | ||||||
| G = 14 dB, VO = 100 mVPP | 625 | MHz | ||||||
| G = 20 dB, VO = 100 mVPP | 260 | MHz | ||||||
| Gain-bandwidth product | G = 20 dB | 3 | GHz | |||||
| Bandwidth for 0.1-dB flatness | G = 10 dB, VO = 1 VPP | 400 | MHz | |||||
| Large-signal bandwidth | G = 10 dB, VO = 1 VPP | 1.5 | GHz | |||||
| Slew rate (differential) | 2-V step | 3500 | V/μs | |||||
| Rise time | 0.25 | ns | ||||||
| Fall time | 0.25 | |||||||
| Settling time to 1% | 1 | |||||||
| Settling time to 0.1% | 10 | |||||||
| 2nd-order harmonic distortion | f = 10 MHz | –107 | dBc | |||||
| f = 50 MHz | –83 | |||||||
| f = 100 MHz | –60 | |||||||
| 3rd-order harmonic distortion | f = 10 MHz | –87 | dBc | |||||
| f = 50 MHz | –65 | |||||||
| f = 100 MHz | –54 | |||||||
| 2nd-order intermodulation distortion | 200-kHz tone spacing, RL = 499 Ω |
fC = 70 MHz | –77 | dBc | ||||
| fC = 140 MHz | –54 | |||||||
| 3rd-order intermodulation distortion | fC = 70 MHz | –77 | ||||||
| fC = 140 MHz | –62 | |||||||
| 2nd-order output intercept point | 200-kHz tone spacing RL = 100 Ω |
fC = 70 MHz | 72 | dBm | ||||
| fC = 140 MHz | 52 | |||||||
| 3rd-order output intercept point | fC = 70 MHz | 38.5 | ||||||
| fC = 140 MHz | 30 | |||||||
| 1-dB compression point | fC = 70 MHz | 2.2 | dBm | |||||
| fC = 140 MHz | 0.25 | |||||||
| Noise figure | 50 Ω system, 10 MHz | 17.1 | dB | |||||
| Input voltage noise | f > 10 MHz | 1.9 | nV/√Hz | |||||
| Input current noise | f > 10 MHz | 2.2 | pA/√Hz | |||||
| DC PERFORMANCE | ||||||||
| Open-loop voltage gain (AOL) | C | 68 | dB | |||||
| Input offset voltage | TA = +25°C | 1 | mV | |||||
| Average offset voltage drift | TA = –40°C to +85°C | 2.6 | μV/°C | |||||
| Input bias current | TA = +25°C | 6 | μA | |||||
| Average bias current drift | TA = –40°C to +85°C | 20 | nA/°C | |||||
| Input offset current | TA = +25°C | 1.6 | μA | |||||
| Average offset current drift | TA = –40°C to +85°C | 4 | nA/°C | |||||
| INPUT | ||||||||
| Common-mode input range high | B | 0.4 | V | |||||
| Common-mode input range low | –0.4 | |||||||
| Common-mode rejection ratio | 80 | dB | ||||||
| Differential input impedance | C | 1.3 || 1.8 | MΩ || pF | |||||
| Common-mode input impedance | C | 1.0 || 2.3 | MΩ || pF | |||||
| OUTPUT | ||||||||
| Maximum output voltage high | Each output with 100 Ω to midsupply | TA = +25°C | C | 0.45 | V | |||
| Minimum output voltage low | TA = +25°C | –0.45 | V | |||||
| Differential output voltage swing | 1.8 | V | ||||||
| Differential output current drive | RL = 10 Ω | 50 | mA | |||||
| Output balance error | VO = 100 mV, f = 1 MHz | –49 | dB | |||||
| Closed-loop output impedance | f = 1 MHz | 0.3 | Ω | |||||
| OUTPUT COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE CONTROL | ||||||||
| Small-signal bandwidth | C | 570 | MHz | |||||
| Slew rate | 60 | V/μs | ||||||
| Gain | 1 | V/V | ||||||
| Output common-mode offset from CM input |
1.25 V < CM < 3.5 V | 4 | mV | |||||
| CM input bias current | 1.25 V < CM < 3.5 V | ±40 | μA | |||||
| CM input voltage high | 1.5 | V | ||||||
| CM input voltage low | –1.5 | |||||||
| CM input impedance | 20 || 1 | kΩ || pF | ||||||
| CM default voltage | 0 | V | ||||||
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||||
| Specified operating voltage | C | 3 | V | |||||
| Quiescent current | TA = +25°C | A | 34.8 | mA | ||||
| Power-supply rejection (±PSRR) | C | 70 | dB | |||||
| POWER-DOWN Referenced to VS– | ||||||||
| Enable voltage threshold | Assured on above 2.1 V + VS– | C | > 2.1 + VS– | V | ||||
| Disable voltage threshold | Assured off below 0.7 V + VS– | < 0.7 + VS- | V | |||||
| Power-down quiescent current | 0.46 | mA | ||||||
| Input bias current | PD = VS– | 65 | μA | |||||
| Input impedance | 50 || 2 | kΩ || pF | ||||||
| Turnon time delay | Measured to output on | 100 | ns | |||||
| Turnoff time delay | Measured to output off | 10 | μs | |||||
(1) Test levels: (A) 100% tested at +25°C. Over-temperature limits by characterization and simulation. (B) Limits set by characterization and simulation. (C) Typical value only for information.
7.7 Dissipation Ratings
| PACKAGE | θJC | θJA | POWER RATING | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA ≤ +25°C | TA = +85°C | |||
| RGT (16) | 2.4°C/W | 39.5°C/W | 2.3 W | 225 mW |
7.8 Typical Characteristics
7.8.1 Typical Characteristics: VS+ – VS– = 5 V
Test conditions at VS+ = +2.5 V, VS– = –2.5V, CM = open, VO = 2 VPP, RF = 349 Ω, RL = 200-Ω differential, G = 10 dB, single-ended input, and input and output referenced to midrail, unless otherwise noted.Table 1. Table of Graphs
| FIGURE | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Small-Signal Frequency Response | Figure 1 | ||
| Large-Signal Frequency Response | Figure 2 | ||
| Harmonic Distortion |
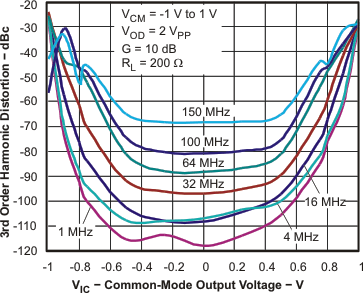
HD2, G = 6 dB, VOD = 2 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 3 |
| HD3, G = 6 dB, VOD = 2 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 4 | |
| HD2, G = 10 dB, VOD = 2 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 5 | |
| HD3, G = 10 dB, VOD = 2 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 6 | |
| HD2, G = 14 dB, VOD = 2 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 7 | |
| HD3, G = 14 dB, VOD = 2 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 8 | |
| HD2, G = 10 dB | vs Output Voltage | Figure 9 | |
| HD3, G = 10 dB | vs Output Voltage | Figure 10 | |
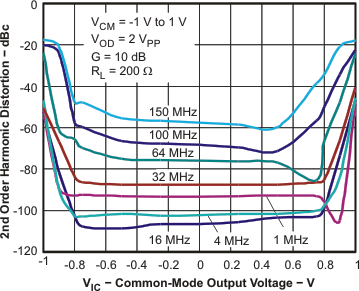
| HD2, G = 10 dB | vs Common-Mode Input Voltage | Figure 11 | |
| HD3, G = 10 dB | vs Common-Mode Input Voltage | Figure 12 | |
| Intermodulation Distortion |
IMD2, G = 6 dB, VOD = 2 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 13 |
| IMD3, G = 6 dB, VOD = 2 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 14 | |
| IMD2, G = 10 dB, VOD = 2 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 15 | |
| IMD3, G = 10 dB, VOD = 2 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 16 | |
| IMD2, G = 14 dB, VOD = 2 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 17 | |
| IMD3, G = 14 dB, VOD = 2 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 18 | |
| Output Intercept Point | OIP2 | vs Frequency | Figure 19 |
| OIP3 | vs Frequency | Figure 20 | |
| 0.1-dB Flatness | Figure 21 | ||
| S-Parameters | vs Frequency | Figure 22 | |
| Transition Rate | vs Output Voltage | Figure 23 | |
| Transient Response | Figure 24 | ||
| Settling Time | Figure 25 | ||
| Rejection Ratio | vs Frequency | Figure 26 | |
| Output Impedance | vs Frequency | Figure 27 | |
| Overdrive Recovery | Figure 28 | ||
| Output Voltage Swing | vs Load Resistance | Figure 29 | |
| Turnoff Time | Figure 30 | ||
| Turnon Time | Figure 31 | ||
| Input Offset Voltage | vs Input Common-Mode Voltage | Figure 32 | |
| Open-Loop Gain | vs Frequency | Figure 33 | |
| Input-Referred Noise | vs Frequency | Figure 34 | |
| Noise Figure | vs Frequency | Figure 35 | |
| Quiescent Current | vs Supply Voltage | Figure 36 | |
| Power-Supply Current | vs Supply Voltage in Power-Down Mode | Figure 37 | |
| Output Balance Error | vs Frequency | Figure 38 | |
| CM Input Impedance | vs Frequency | Figure 39 | |
| CM Small-Signal Frequency Response | Figure 40 | ||
| CM Input Bias Current | vs CM Input Voltage | Figure 41 | |
| Differential Output Offset Voltage | vs CM Input Voltage | Figure 42 | |
| Output Common-Mode Offset | vs CM Input Voltage | Figure 43 | |
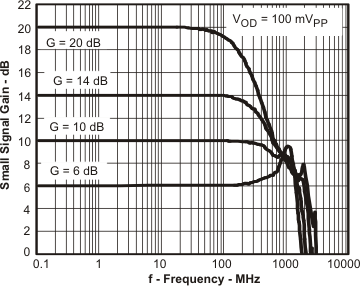 Figure 1. Small-Signal Frequency Response
Figure 1. Small-Signal Frequency Response
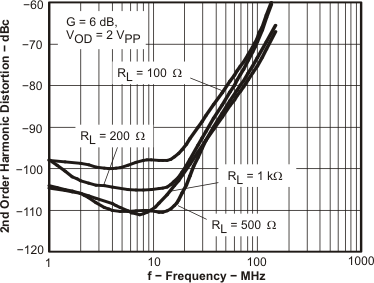 Figure 3. HD2 vs Frequency
Figure 3. HD2 vs Frequency
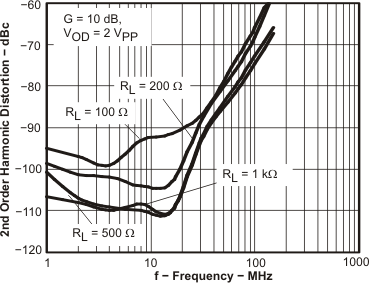 Figure 5. HD2 vs Frequency
Figure 5. HD2 vs Frequency
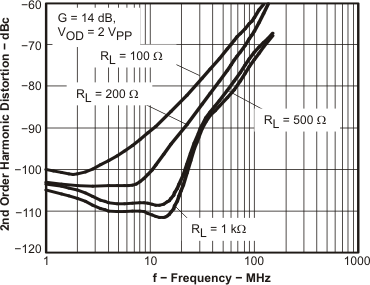 Figure 7. HD2 vs Frequency
Figure 7. HD2 vs Frequency
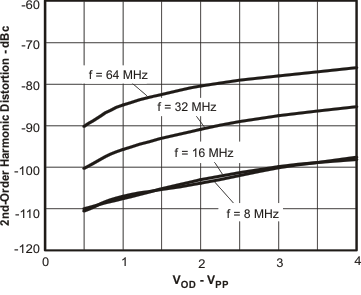 Figure 9. HD2 vs Output Voltage
Figure 9. HD2 vs Output Voltage
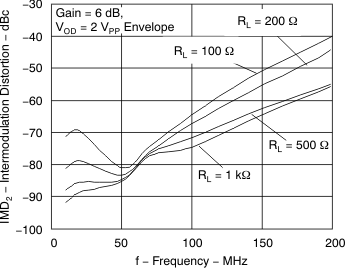 Figure 13. IMD2 vs Frequency
Figure 13. IMD2 vs Frequency
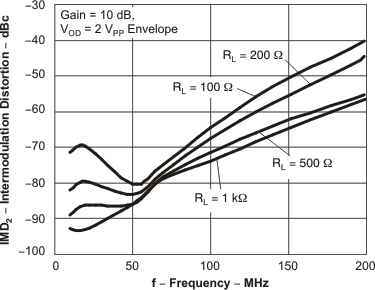 Figure 15. IMD2 vs Frequency
Figure 15. IMD2 vs Frequency
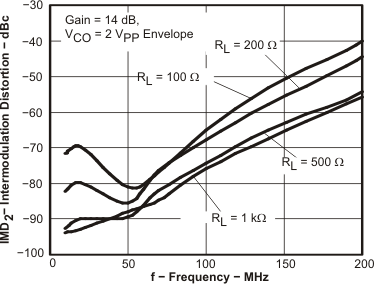 Figure 17. IMD2 vs Frequency
Figure 17. IMD2 vs Frequency
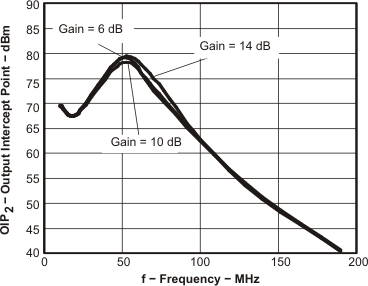 Figure 19. OIP2 vs Frequency
Figure 19. OIP2 vs Frequency
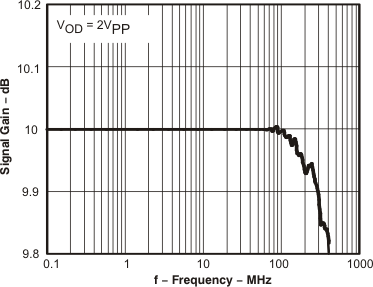 Figure 21. 0.1-dB Flatness
Figure 21. 0.1-dB Flatness
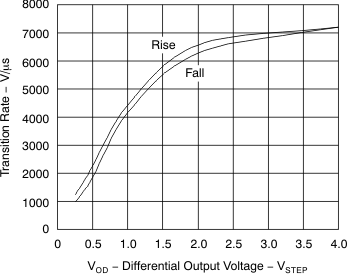 Figure 23. Transition Rate vs Output Voltage
Figure 23. Transition Rate vs Output Voltage
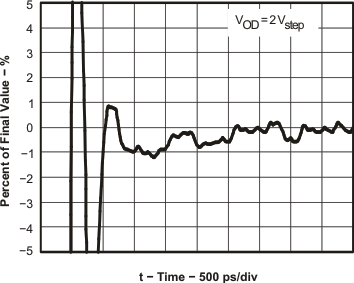 Figure 25. Settling Time
Figure 25. Settling Time
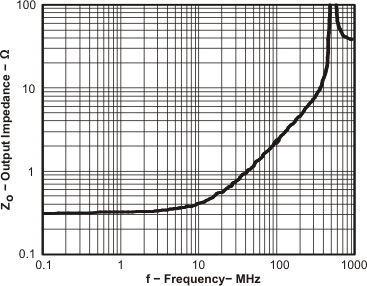 Figure 27. Output Impedance vs Frequency
Figure 27. Output Impedance vs Frequency
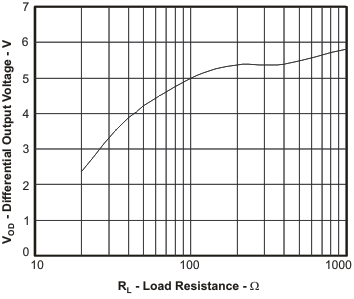 Figure 29. Output Voltage Swing vs Load Resistance
Figure 29. Output Voltage Swing vs Load Resistance
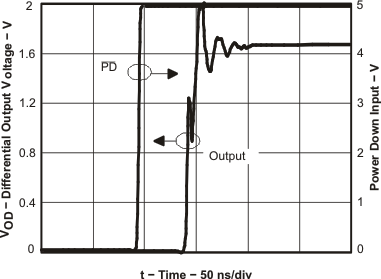 Figure 31. Turnon Time
Figure 31. Turnon Time
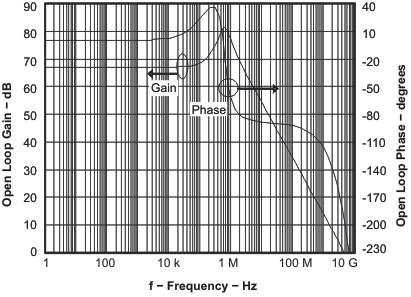 Figure 33. Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs Frequency
Figure 33. Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs Frequency
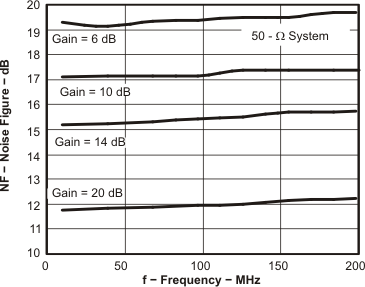 Figure 35. Noise Figure vs Frequency
Figure 35. Noise Figure vs Frequency
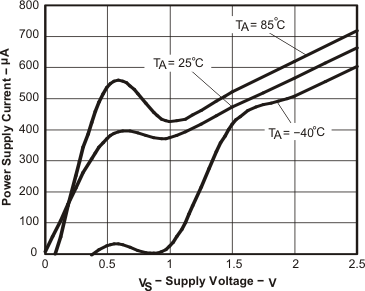 Figure 37. Power-Supply Current vs Supply Voltage in Power-Down Mode
Figure 37. Power-Supply Current vs Supply Voltage in Power-Down Mode
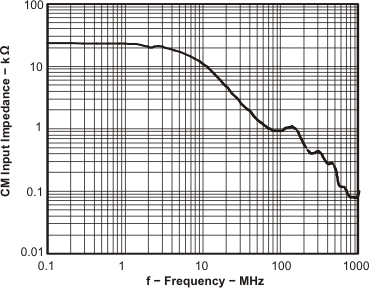 Figure 39. CM Input Impedance vs Frequency
Figure 39. CM Input Impedance vs Frequency
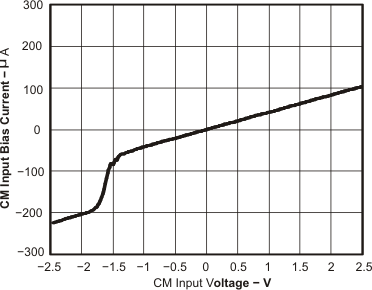 Figure 41. CM Input Bias Current vs CM Input Voltage
Figure 41. CM Input Bias Current vs CM Input Voltage
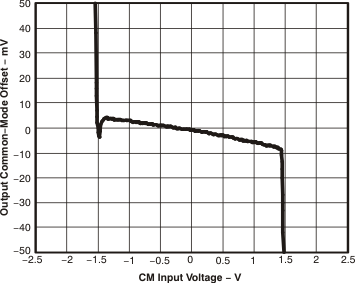 Figure 43. Output Common-Mode Offset vs CM Input Voltage
Figure 43. Output Common-Mode Offset vs CM Input Voltage
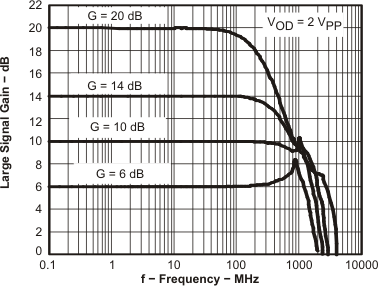 Figure 2. Large-Signal Frequency Response
Figure 2. Large-Signal Frequency Response
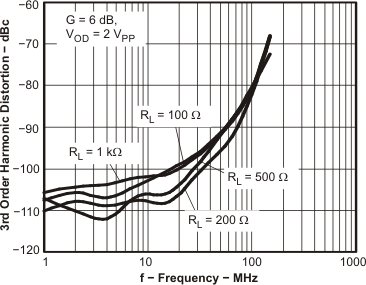 Figure 4. HD3 vs Frequency
Figure 4. HD3 vs Frequency
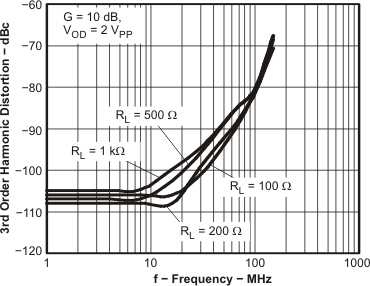 Figure 6. HD3 vs Frequency
Figure 6. HD3 vs Frequency
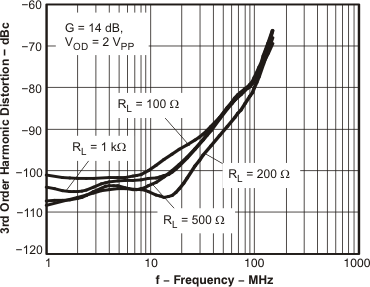 Figure 8. HD3 vs Frequency
Figure 8. HD3 vs Frequency
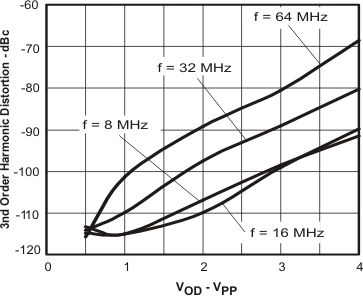 Figure 10. HD3 vs Output Voltage
Figure 10. HD3 vs Output Voltage
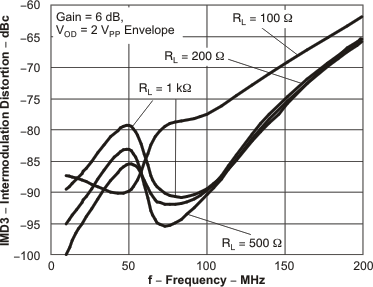 Figure 14. IMD3 vs Frequency
Figure 14. IMD3 vs Frequency
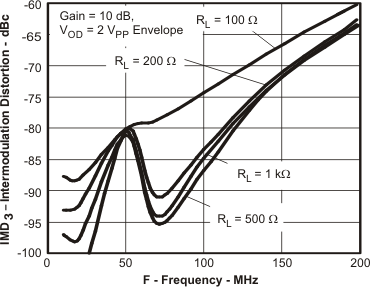 Figure 16. IMD3 vs Frequency
Figure 16. IMD3 vs Frequency
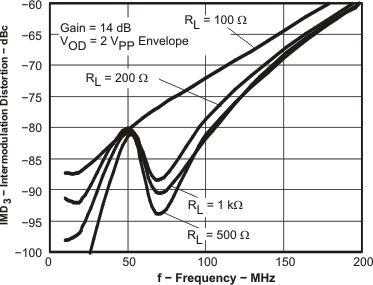 Figure 18. IMD3 vs Frequency
Figure 18. IMD3 vs Frequency
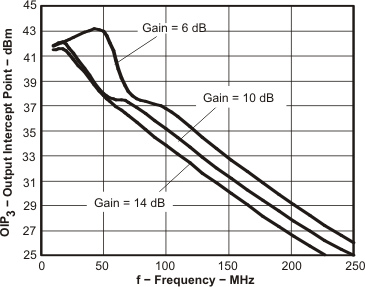 Figure 20. OIP3 vs Frequency
Figure 20. OIP3 vs Frequency
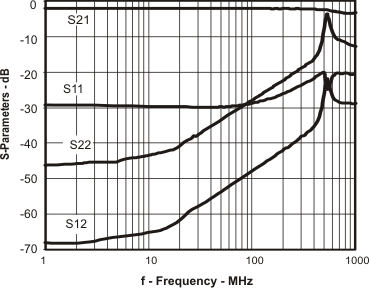 Figure 22. S-Parameters vs Frequency
Figure 22. S-Parameters vs Frequency
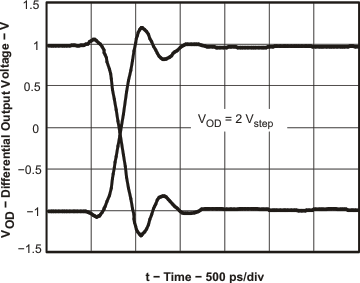 Figure 24. Transient Response
Figure 24. Transient Response
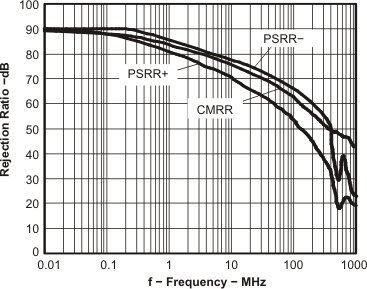 Figure 26. Rejection Ratio vs Frequency
Figure 26. Rejection Ratio vs Frequency
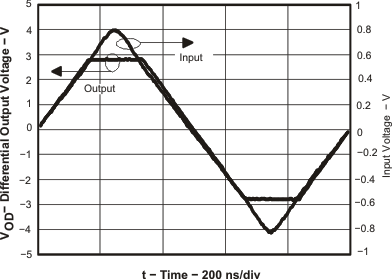 Figure 28. Overdrive Recovery
Figure 28. Overdrive Recovery
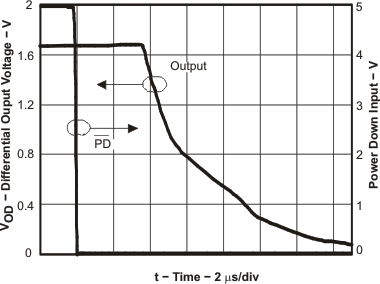 Figure 30. Turnoff Time
Figure 30. Turnoff Time
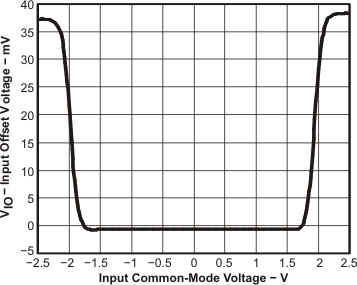 Figure 32. Input Offset Voltage vs Input Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 32. Input Offset Voltage vs Input Common-Mode Voltage
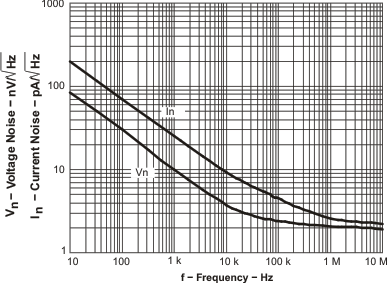 Figure 34. Input-Referred Noise vs Frequency
Figure 34. Input-Referred Noise vs Frequency
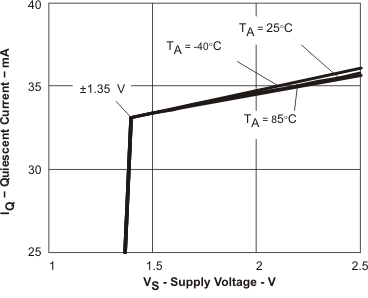 Figure 36. Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 36. Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage
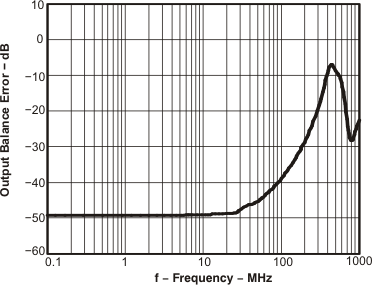 Figure 38. Output Balance Error vs Frequency
Figure 38. Output Balance Error vs Frequency
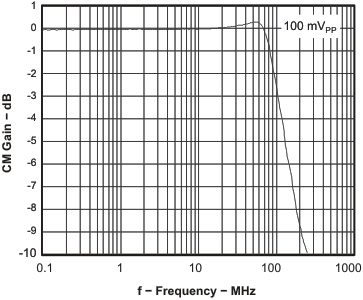 Figure 40. CM Small-Signal Frequency Response
Figure 40. CM Small-Signal Frequency Response
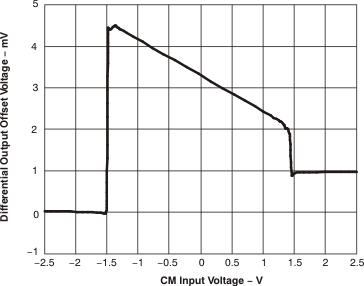 Figure 42. Differential Output Offset Voltage vs CM Input Voltage
Figure 42. Differential Output Offset Voltage vs CM Input Voltage
7.8.2 Typical Characteristics: VS+ – VS– = 3 V
Test conditions at VS+ = +1.5 V, VS– = –1.5 V, CM = open, VOD = 1 VPP, RF = 349 Ω, RL = 200-Ω differential, G = 10 dB, single-ended input, and input and output referenced to midrail, unless otherwise noted.Table 2. Table of Graphs
| FIGURE | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Small-Signal Frequency Response | Figure 44 | ||
| Large-Signal Frequency Response | Figure 45 | ||
| Harmonic Distortion |
HD2, G = 6 dB, VOD = 1 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 46 |
| HD3, G = 6 dB, VOD = 1 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 47 | |
| HD2, G = 10 dB, VOD = 1 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 48 | |
| HD3, G = 10 dB, VOD = 1 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 49 | |
| HD2, G = 14 dB, VOD = 1 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 50 | |
| HD3, G = 14 dB, VOD = 1 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 51 | |
| Intermodulation Distortion |
IMD2, G = 6 dB, VOD = 1 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 52 |
| IMD3, G = 6 dB, VOD = 1 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 53 | |
| IMD2, G = 10 dB, VOD = 1 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 54 | |
| IMD3, G = 10 dB, VOD = 1 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 55 | |
| IMD2, G = 14 dB, VOD = 1 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 56 | |
| IMD3, G = 14 dB, VOD = 1 VPP | vs Frequency | Figure 57 | |
| Output Intercept Point | OIP2 | vs Frequency | Figure 58 |
| OIP3 | vs Frequency | Figure 59 | |
| 0.1 dB Flatness | Figure 60 | ||
| S-Parameters | vs Frequency | Figure 61 | |
| Transition Rate | vs Output Voltage | Figure 62 | |
| Transient Response | Figure 63 | ||
| Settling Time | Figure 64 | ||
| Output Voltage Swing | vs Load Resistance | Figure 65 | |
| Rejection Ratio | vs Frequency | Figure 66 | |
| Overdrive Recovery | Figure 67 | ||
| Output Impedance | vs Frequency | Figure 68 | |
| Turnoff Time | Figure 69 | ||
| Turnon Time | Figure 70 | ||
| Output Balance Error | vs Frequency | Figure 71 | |
| Noise Figure | vs Frequency | Figure 72 | |
| CM Input Impedance | vs Frequency | Figure 73 | |
| Differential Output Offset Voltage | vs CM Input Voltage | Figure 74 | |
| Output Common-Mode Offset | vs CM Input Voltage | Figure 75 | |
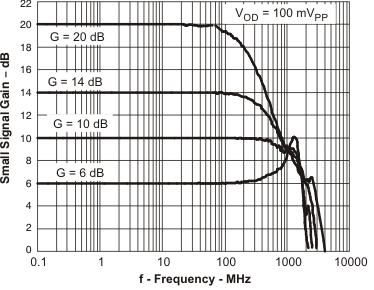 Figure 44. Small-Signal Frequency Response
Figure 44. Small-Signal Frequency Response
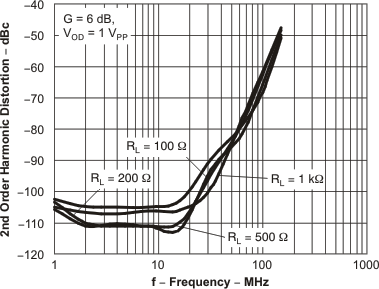 Figure 46. HD2 vs Frequency
Figure 46. HD2 vs Frequency
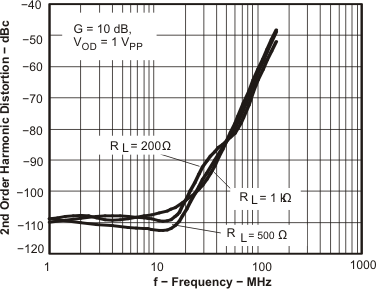 Figure 48. HD2 vs Frequency
Figure 48. HD2 vs Frequency
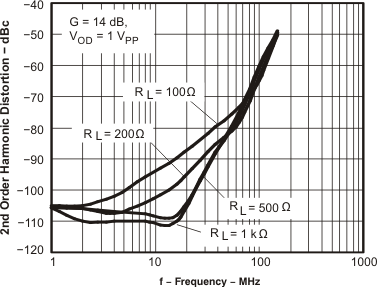 Figure 50. HD2 vs Frequency
Figure 50. HD2 vs Frequency
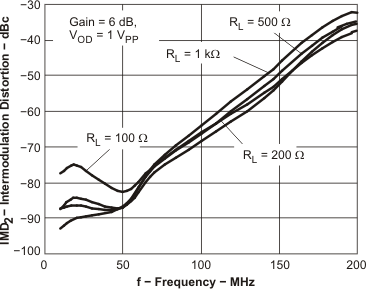 Figure 52. IMD2 vs Frequency
Figure 52. IMD2 vs Frequency
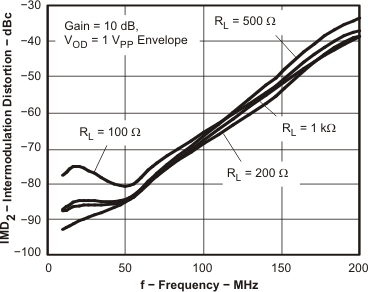 Figure 54. IMD2 vs Frequency
Figure 54. IMD2 vs Frequency
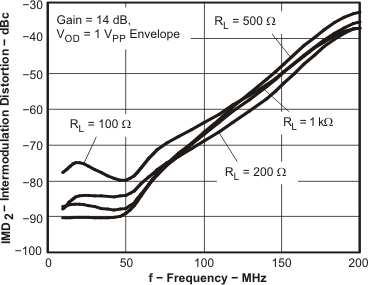 Figure 56. IMD2 vs Frequency
Figure 56. IMD2 vs Frequency
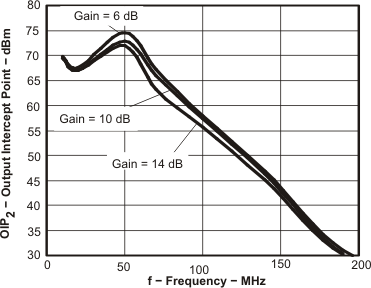 Figure 58. OIP2, dBm vs Frequency
Figure 58. OIP2, dBm vs Frequency
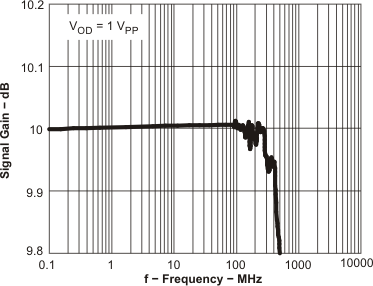 Figure 60. 0.1-dB Flatness
Figure 60. 0.1-dB Flatness
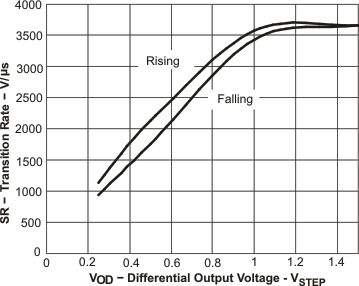 Figure 62. Transition Rate vs Output Voltage
Figure 62. Transition Rate vs Output Voltage
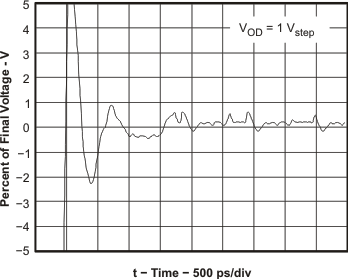 Figure 64. Settling Time
Figure 64. Settling Time
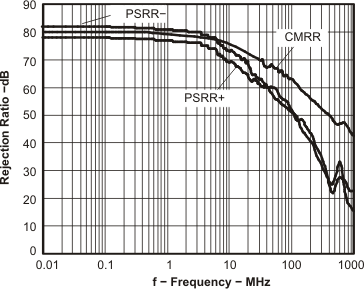 Figure 66. Rejection Ratio vs Frequency
Figure 66. Rejection Ratio vs Frequency
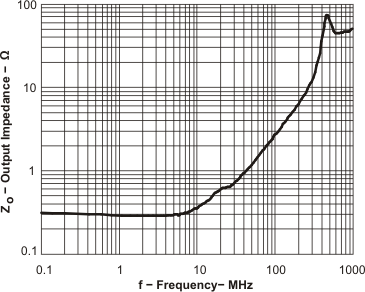 Figure 68. Output Impedance vs Frequency
Figure 68. Output Impedance vs Frequency
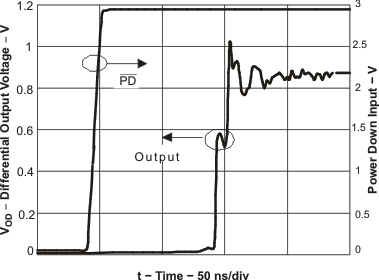 Figure 70. Turnon Time
Figure 70. Turnon Time
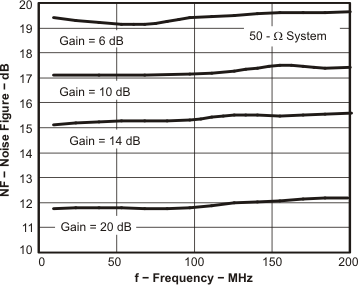 Figure 72. Noise Figure vs Frequency
Figure 72. Noise Figure vs Frequency
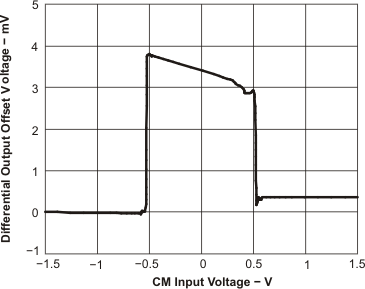 Figure 74. Differential Output Offset Voltage vs CM Input Voltage
Figure 74. Differential Output Offset Voltage vs CM Input Voltage
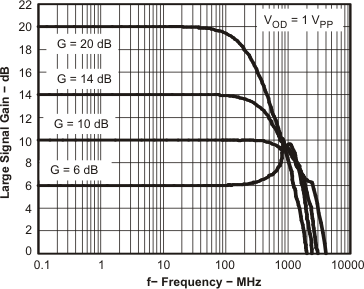 Figure 45. Large-Signal Frequency Response
Figure 45. Large-Signal Frequency Response
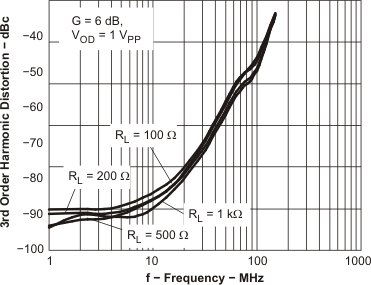 Figure 47. HD3 vs Frequency
Figure 47. HD3 vs Frequency
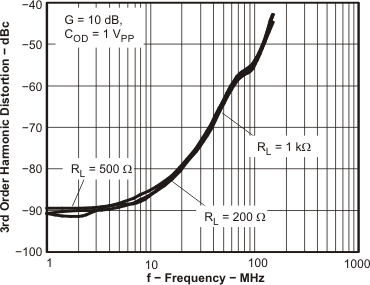 Figure 49. HD3 vs Frequency
Figure 49. HD3 vs Frequency
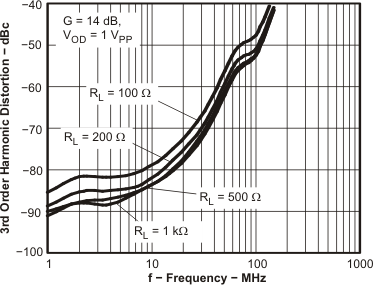 Figure 51. HD3 vs Frequency
Figure 51. HD3 vs Frequency
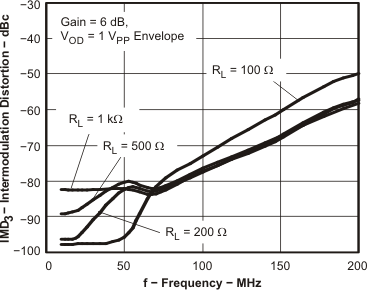 Figure 53. IMD3 vs Frequency
Figure 53. IMD3 vs Frequency
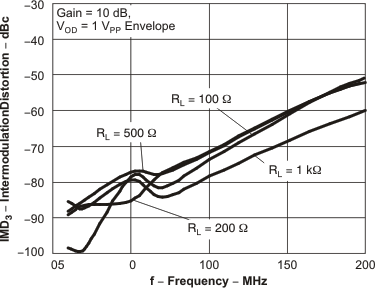 Figure 55. IMD3 vs Frequency
Figure 55. IMD3 vs Frequency
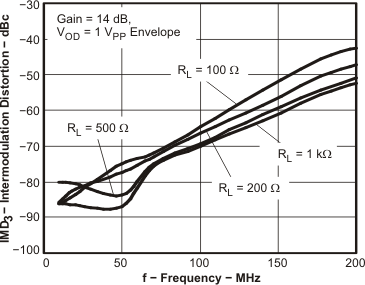 Figure 57. IMD3 vs Frequency
Figure 57. IMD3 vs Frequency
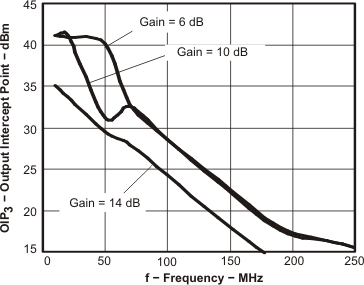 Figure 59. OIP3, dBm vs Frequency
Figure 59. OIP3, dBm vs Frequency
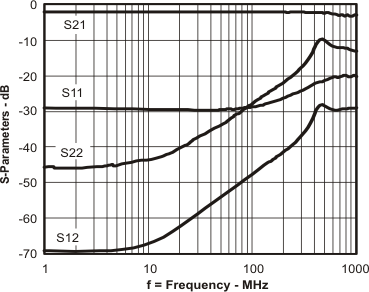 Figure 61. S-Parameters vs Frequency
Figure 61. S-Parameters vs Frequency
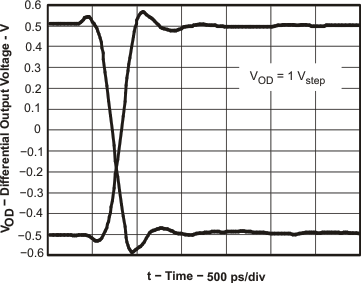 Figure 63. Transient Response
Figure 63. Transient Response
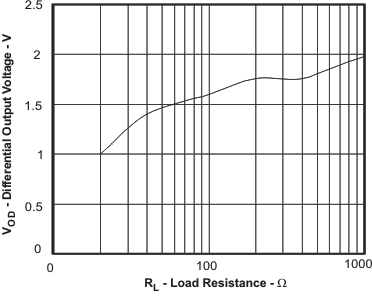 Figure 65. Output Voltage Swing vs Load Resistance
Figure 65. Output Voltage Swing vs Load Resistance
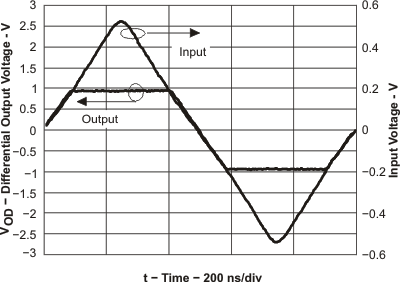 Figure 67. Overdrive Recovery
Figure 67. Overdrive Recovery
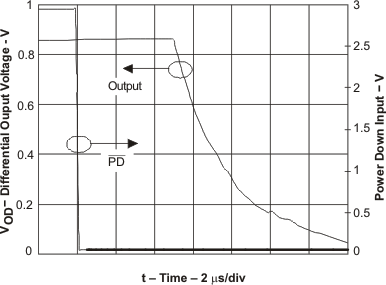 Figure 69. Turnoff Time
Figure 69. Turnoff Time
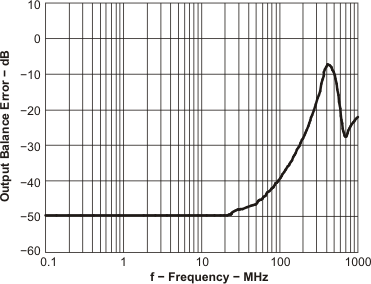 Figure 71. Output Balance Error vs Frequency
Figure 71. Output Balance Error vs Frequency
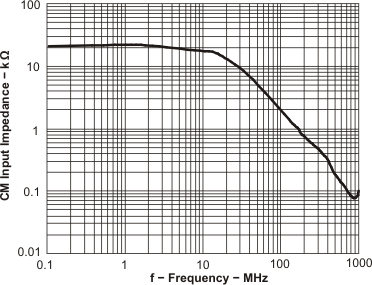 Figure 73. CM Input Impedance vs Frequency
Figure 73. CM Input Impedance vs Frequency
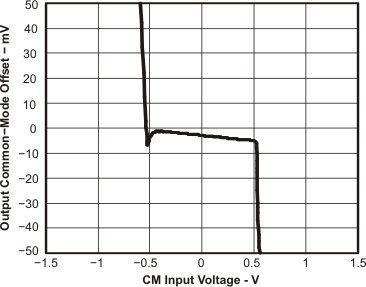 Figure 75. Output Common-Mode Offset vs CM Input Voltage
Figure 75. Output Common-Mode Offset vs CM Input Voltage