ZHCSH83 December 2017 TLV2172-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
Figure 29 shows a unity-gain buffer driving a capacitive load. Equation 1 shows the transfer function for the circuit in Figure 29.Figure 29 does not show the open-loop output resistance of the operational amplifier (Ro).
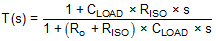
The transfer function in Equation 1 has a pole and a zero. The frequency of the pole (fp) is determined by (Ro + RISO) and CLOAD. The RISO and CLOAD components determine the frequency of the zero (fz). A stable system is obtained by selecting RISO so that the rate of closure (ROC) between the open-loop gain (AOL) and 1/β is 20 dB per decade. Figure 30 shows the concept. The 1/β curve for a unity-gain buffer is 0 dB.
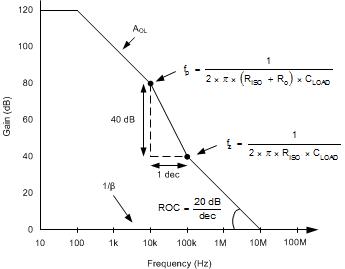 Figure 30. Unity-Gain Amplifier With RISO Compensation
Figure 30. Unity-Gain Amplifier With RISO CompensationTypically, ROC stability analysis is simulated. The validity of the analysis depends on multiple factors, especially the accurate modeling of Ro. In addition to simulating the ROC, a robust stability analysis includes a measurement of overshoot percentage and AC gain peaking of the circuit using a function generator, oscilloscope, and gain and phase analyzer. Phase margin is then calculated from these measurements. Table 3 shows the overshoot percentage and AC gain peaking that correspond to phase margins of 45° and 60°. For more details on this design and other alternative devices that can replace the TLV2172-Q1, see the Capacitive Load Drive Solution Using an Isolation Resistor precision design.
Table 3. Phase Margin versus Overshoot and AC Gain Peaking
| PHASE MARGIN | OVERSHOOT | AC GAIN PEAKING |
|---|---|---|
| 45° | 23.3% | 2.35 dB |
| 60° | 8.8% | 0.28 dB |