SNOSD54 June 2017 LM339-MIL
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封裝選項(xiàng)
機(jī)械數(shù)據(jù) (封裝 | 引腳)
- J|14
散熱焊盤機(jī)械數(shù)據(jù) (封裝 | 引腳)
訂購信息
8 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
8.1 Application Information
The LM339-MIL device is specified for operation from 2 V to 36 V (±1 V to ±18 V) over the temperature range of 0°C to 70°C. While it may seem like a comparator has a well-defined and somewhat limited functionality as a 1-bit ADC, a comparator is a versatile component which can be used for many functions.
8.2 Typical Application
8.2.1 Basic Comparator
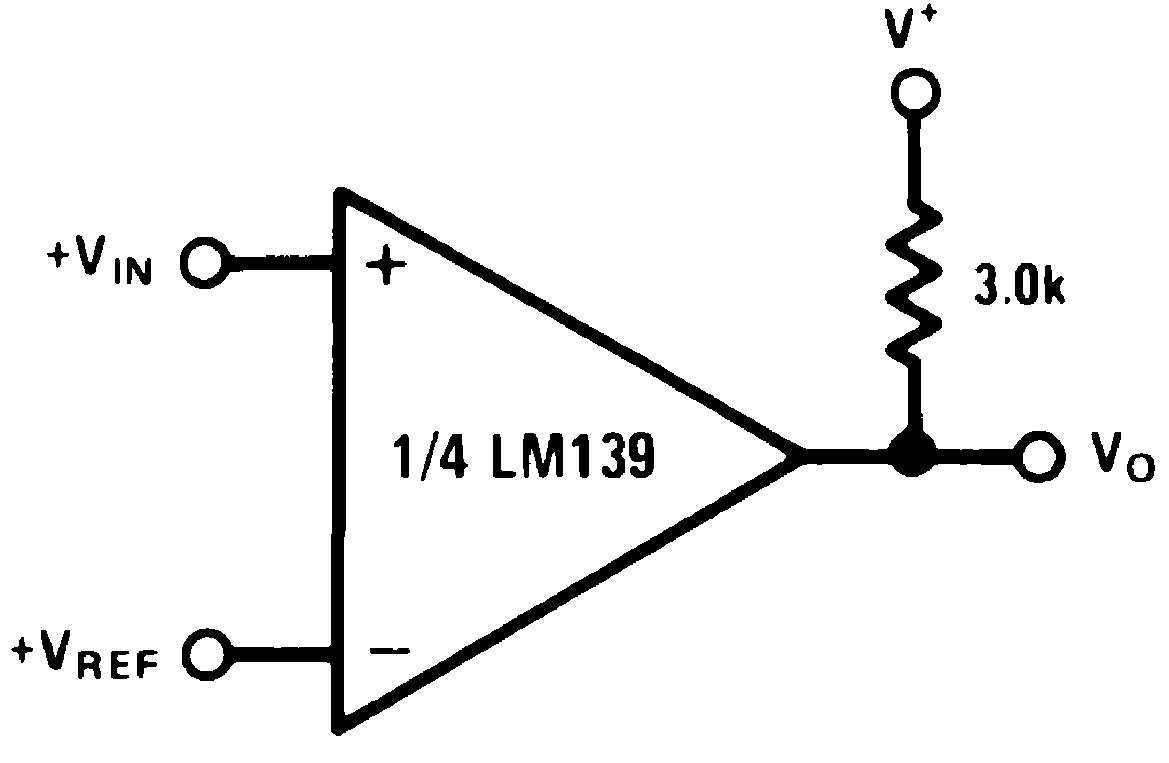 Figure 6. Basic Comparator Schematic
Figure 6. Basic Comparator Schematic
8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
The basic usage of a comparator is to indicate when a specific analog signal has exceeded some predefined threshold. In this application, the negative input is tied to a reference voltage, and the positive input is connected to the input signal. The output is pulled up with a resistor to the logic supply voltage, V+.
For an example application, the supply voltage is 5 V. The input signal varies between 1 V and 3 V. Specifically as an example, to know when the input exceeds 2.5 V, set the VREF voltage to 2.5 V.
8.2.1.2 Application Curve
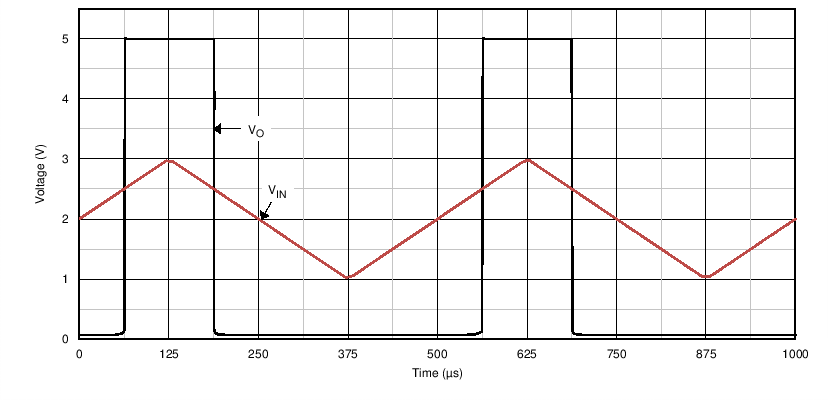 Figure 7. Basic Comparator Response
Figure 7. Basic Comparator Response
8.3 System Examples
 Figure 8. Driving CMOS
Figure 8. Driving CMOS(V+ = 5 VDC)
 Figure 9. Driving TTL
Figure 9. Driving TTL(V+ = 5 VDC)
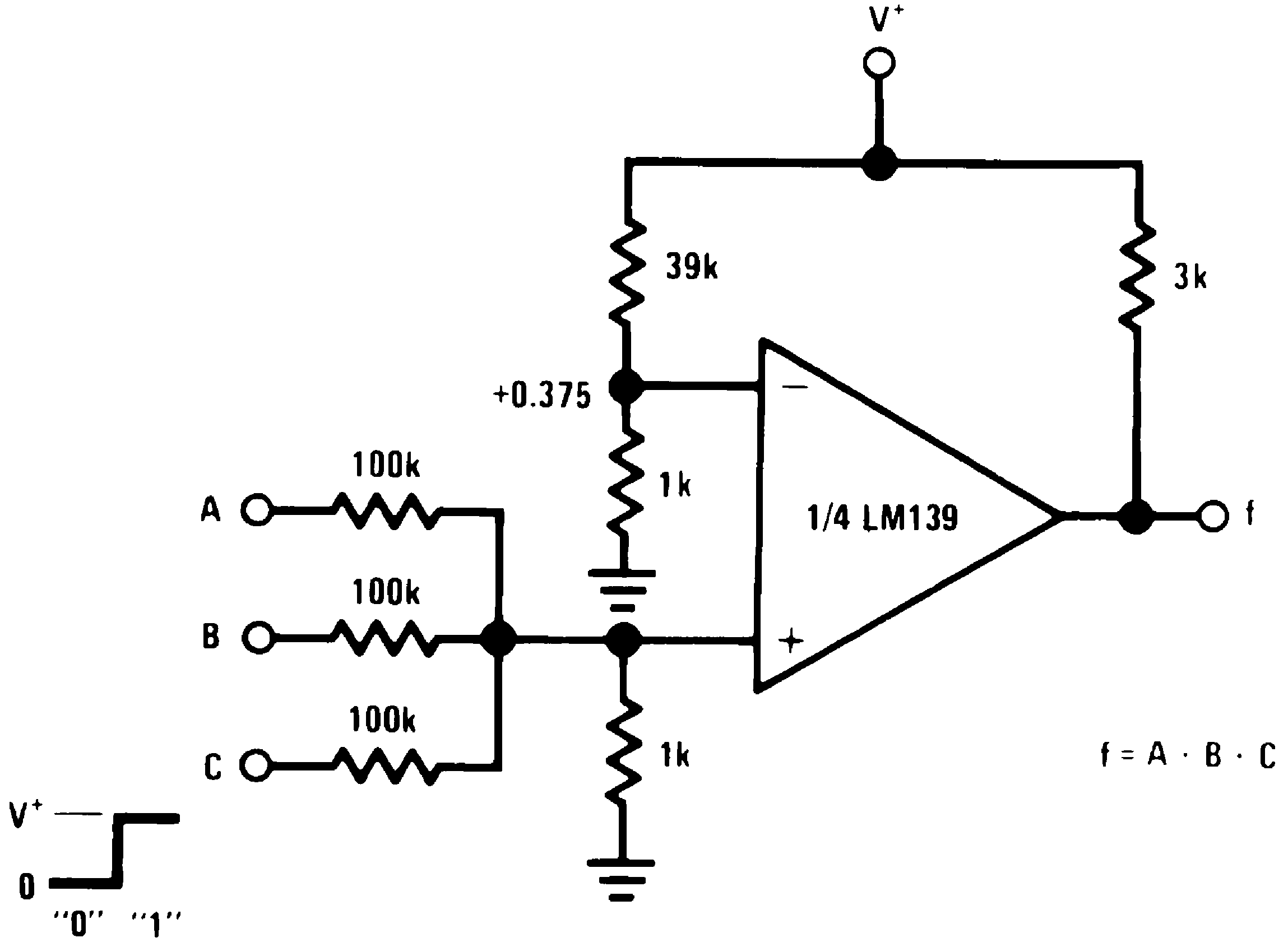 Figure 10. AND Gate
Figure 10. AND Gate(V+ = 5 VDC)
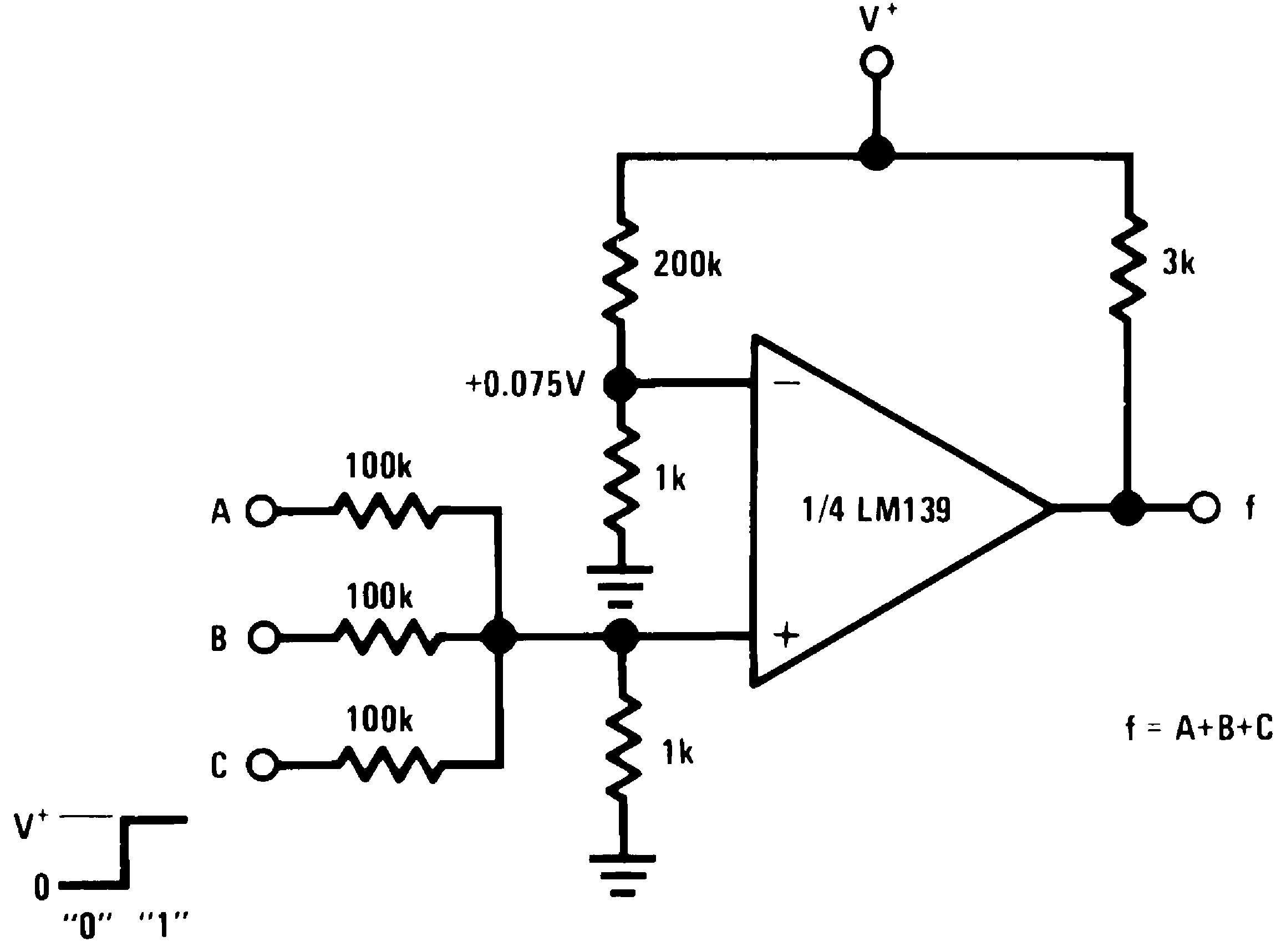 Figure 11. OR Gate
Figure 11. OR Gate(V+ = 5 VDC)
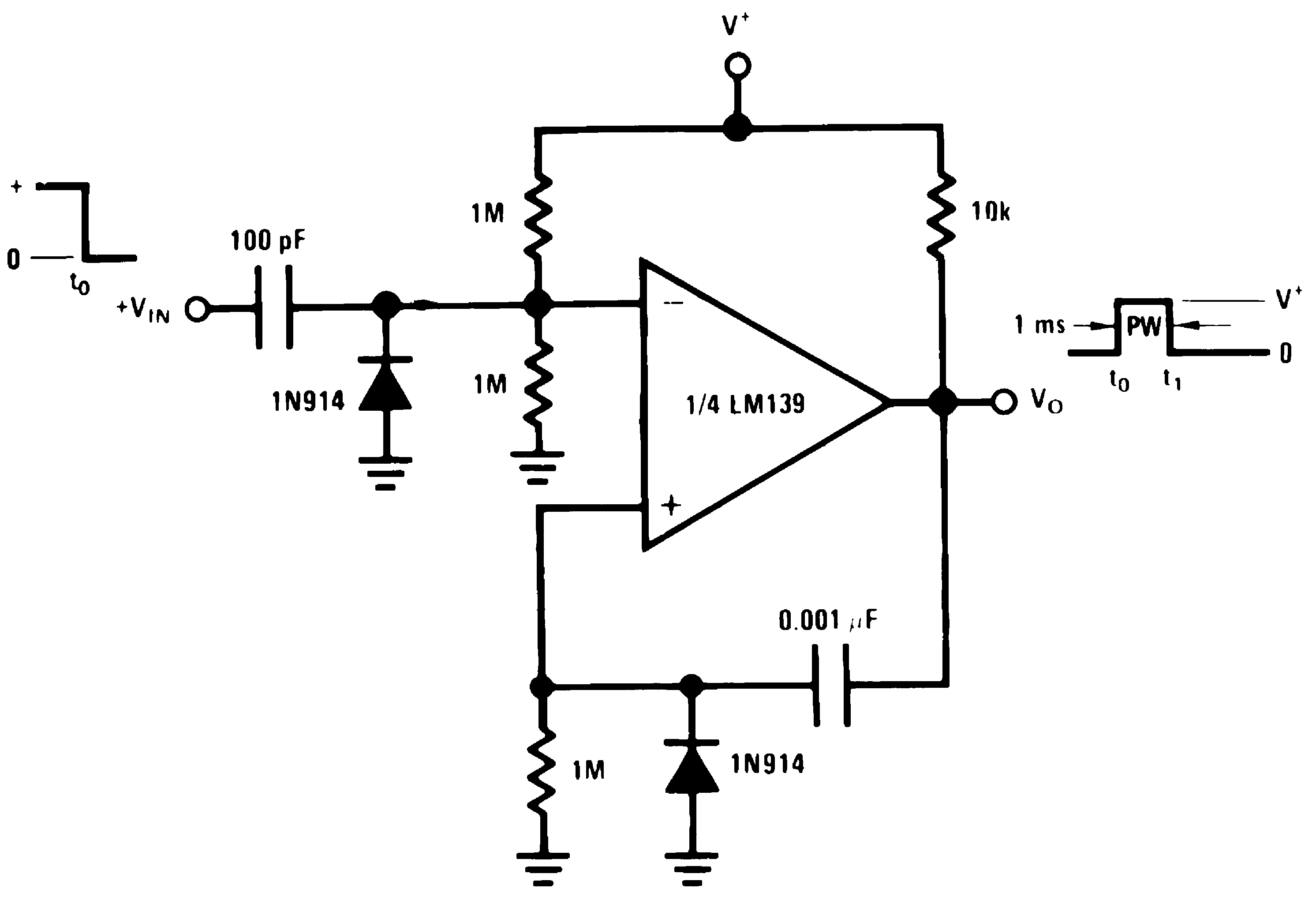 Figure 12. One-Shot Multivibrator
Figure 12. One-Shot Multivibrator(V+= 15 VDC)
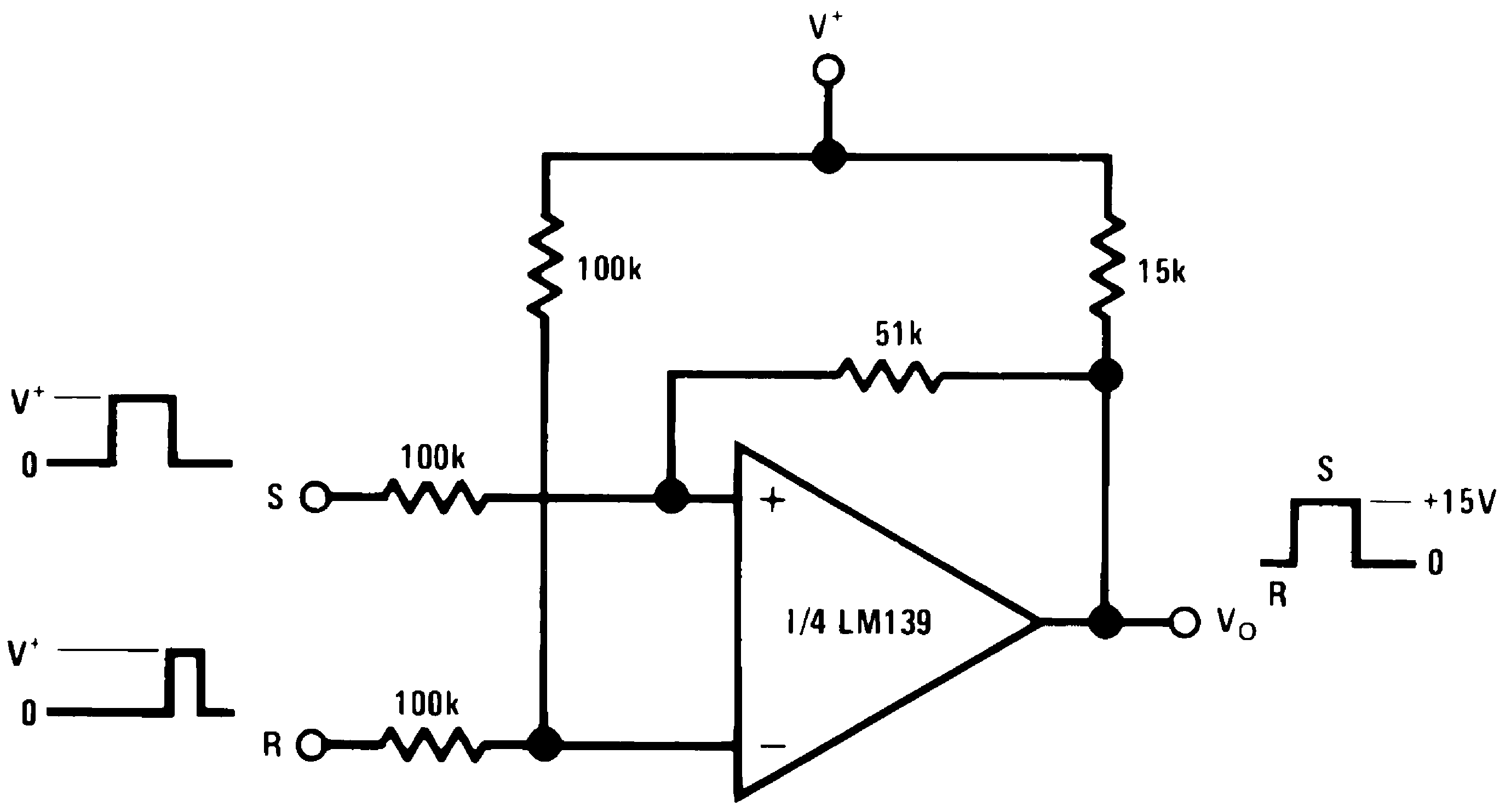 Figure 13. Bi-Stable Multivibrator
Figure 13. Bi-Stable Multivibrator(V+= 15 VDC)
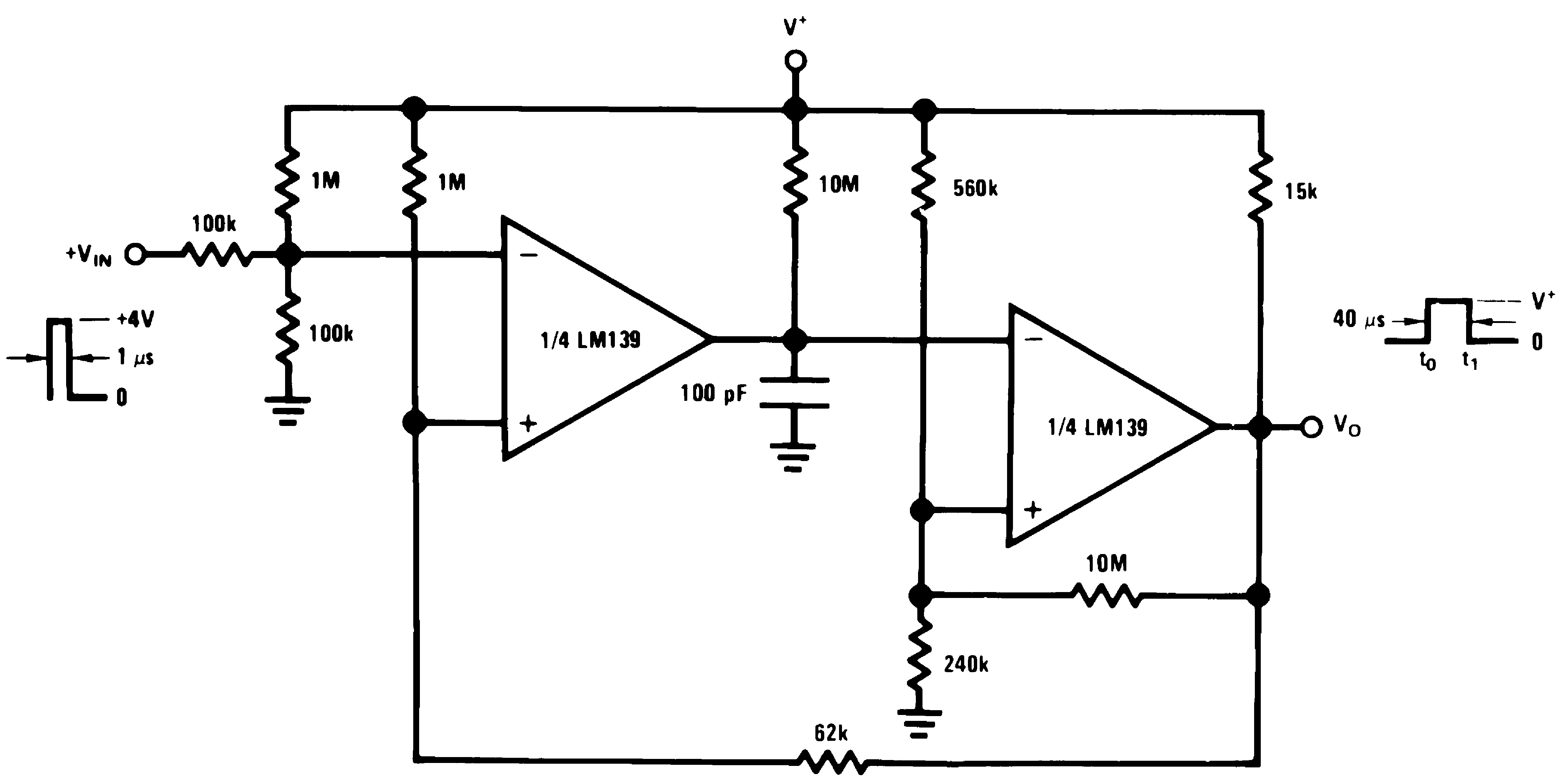 Figure 14. One-Shot Multivibrator With Input Lockout
Figure 14. One-Shot Multivibrator With Input Lockout(V+= 15 VDC)
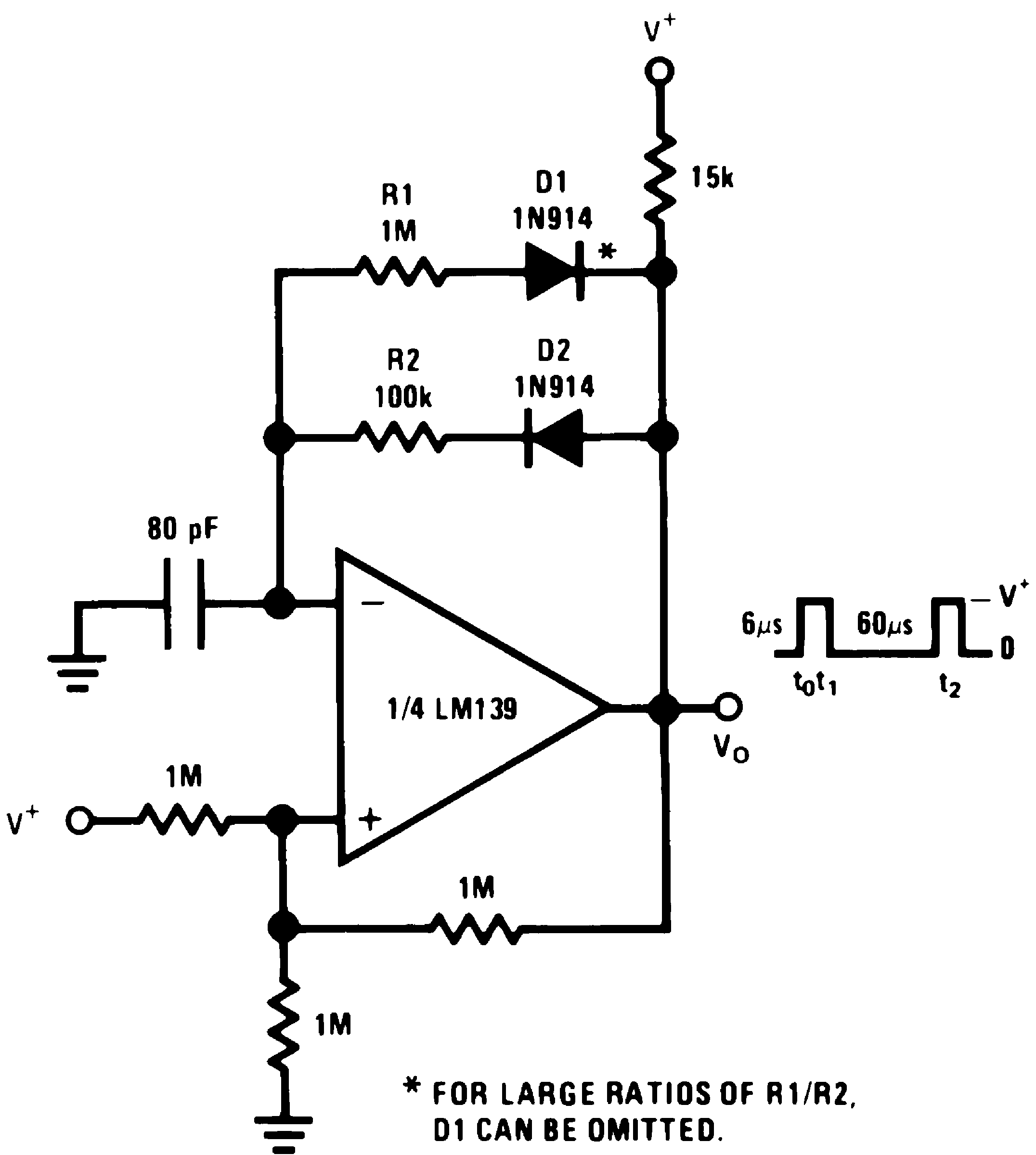 Figure 15. Pulse Generator
Figure 15. Pulse Generator(V+= 15 VDC)
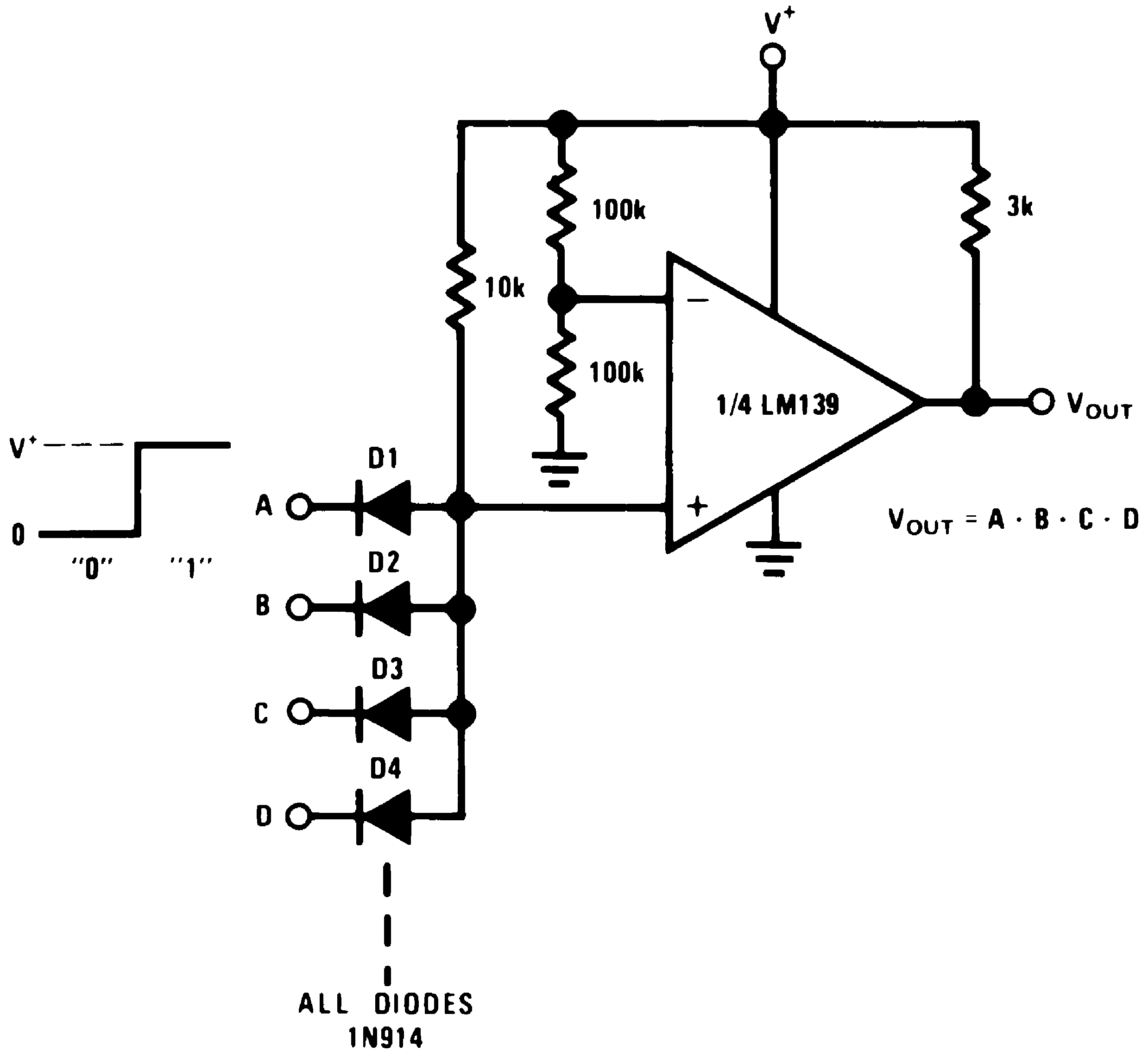 Figure 16. Large Fan-In AND Gate
Figure 16. Large Fan-In AND Gate(V+= 15 VDC)
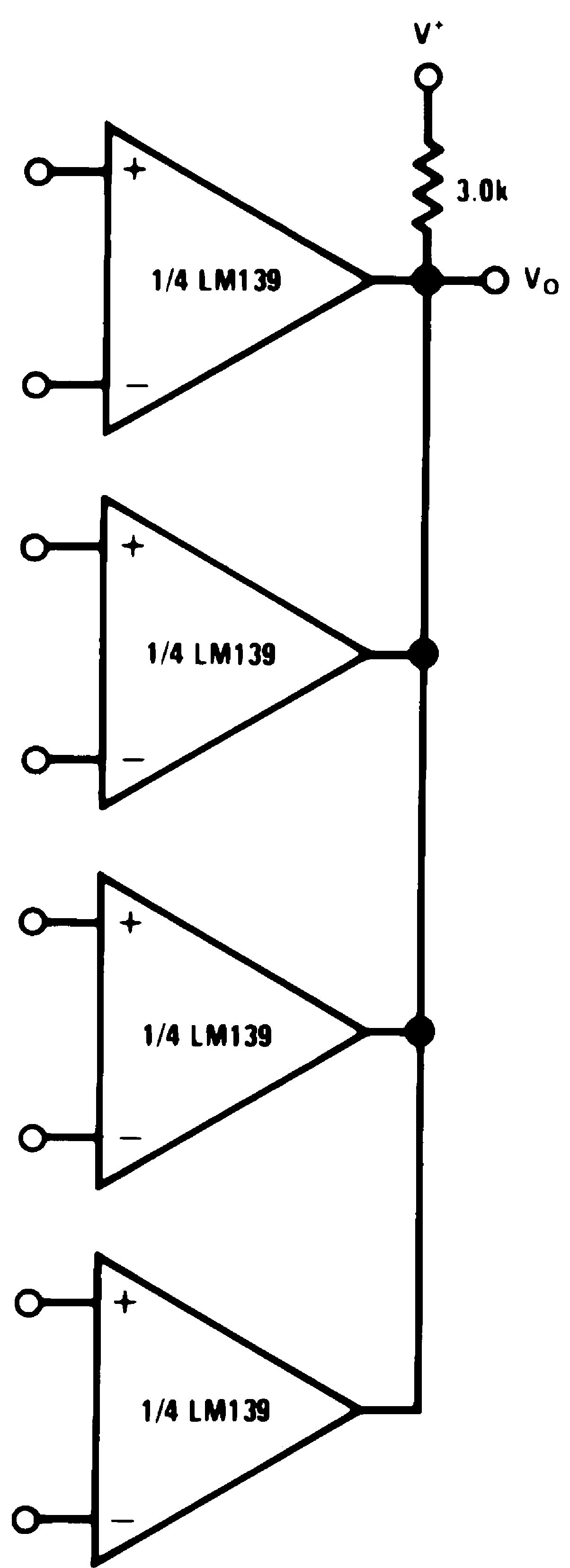 Figure 17. ORing the Outputs
Figure 17. ORing the Outputs(V+= 15 VDC)
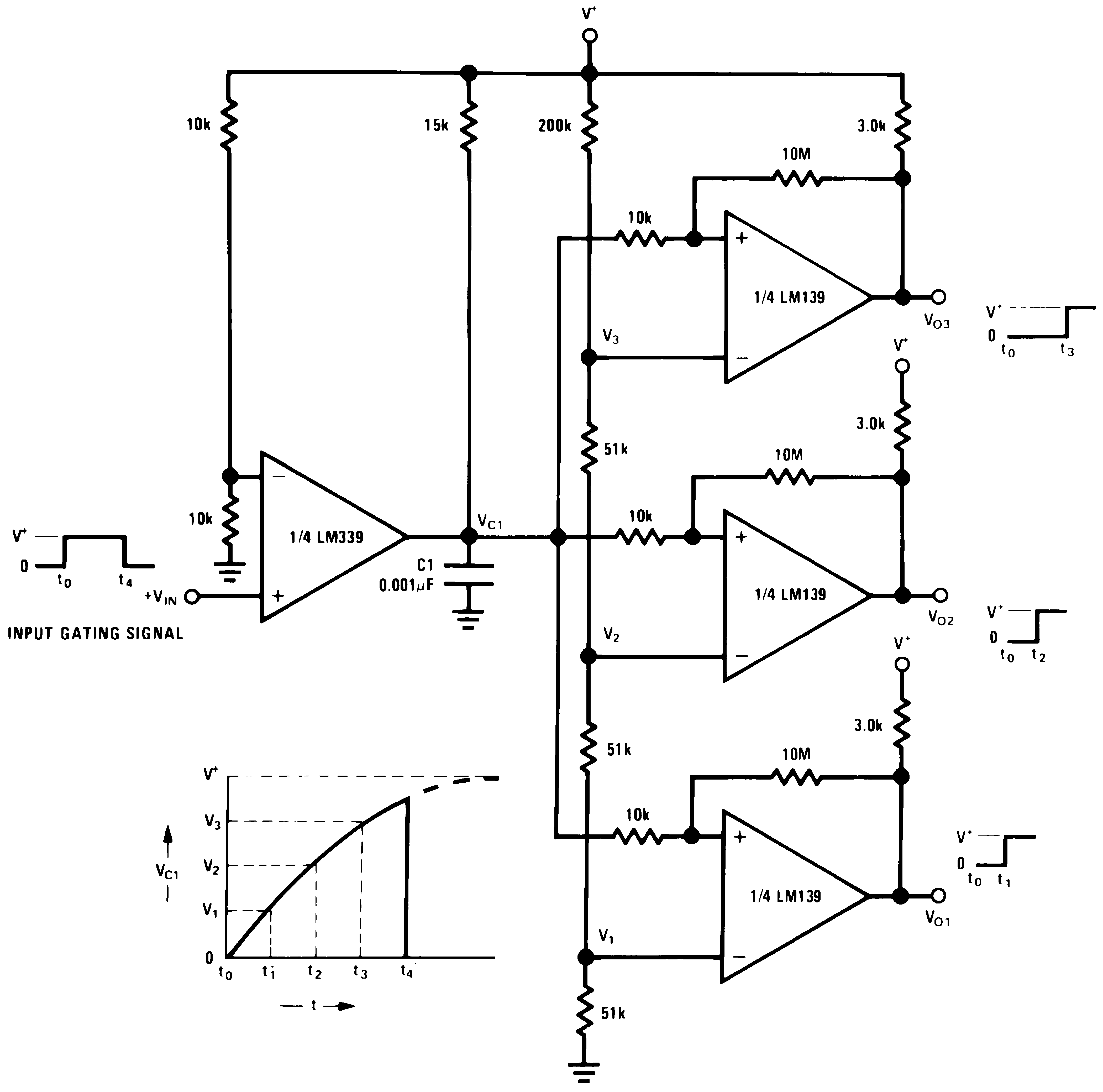 Figure 18. Time Delay Generator
Figure 18. Time Delay Generator(V+= 15 VDC)
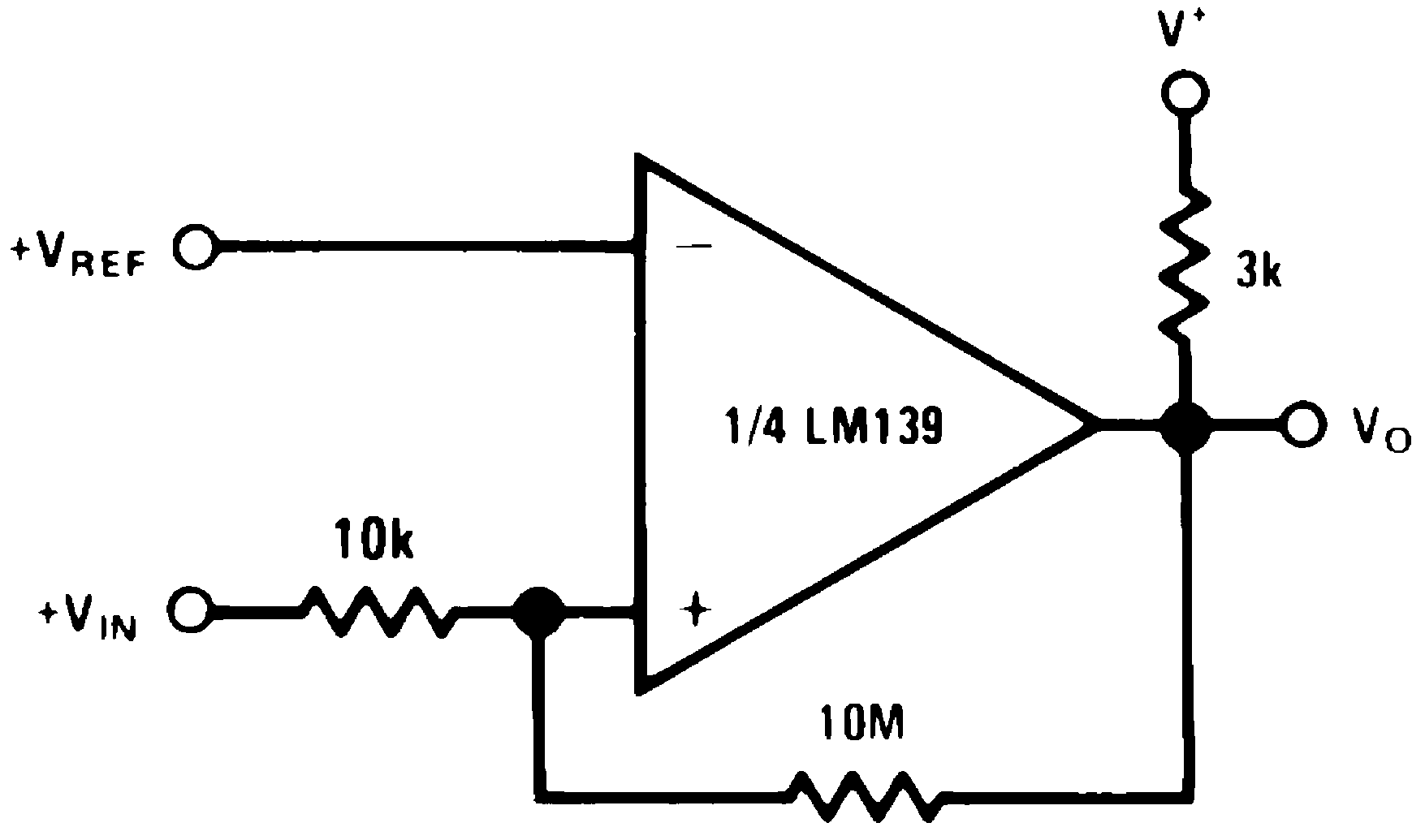 Figure 19. Noninverting Comparator with Hysteresis
Figure 19. Noninverting Comparator with Hysteresis(V+= 15 VDC)
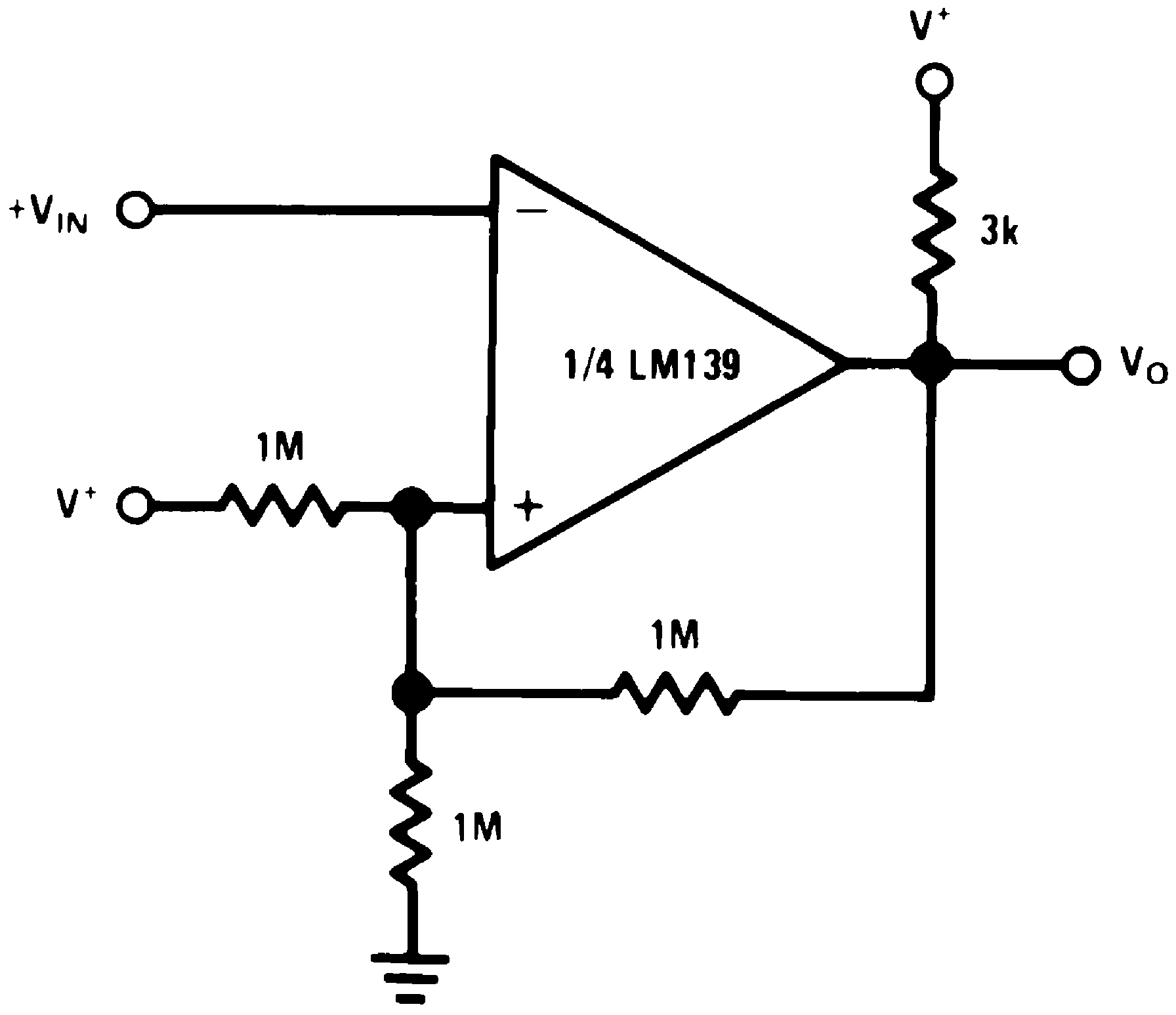 Figure 20. Inverting Comparator With Hysteresis
Figure 20. Inverting Comparator With Hysteresis(V+= 15 VDC)
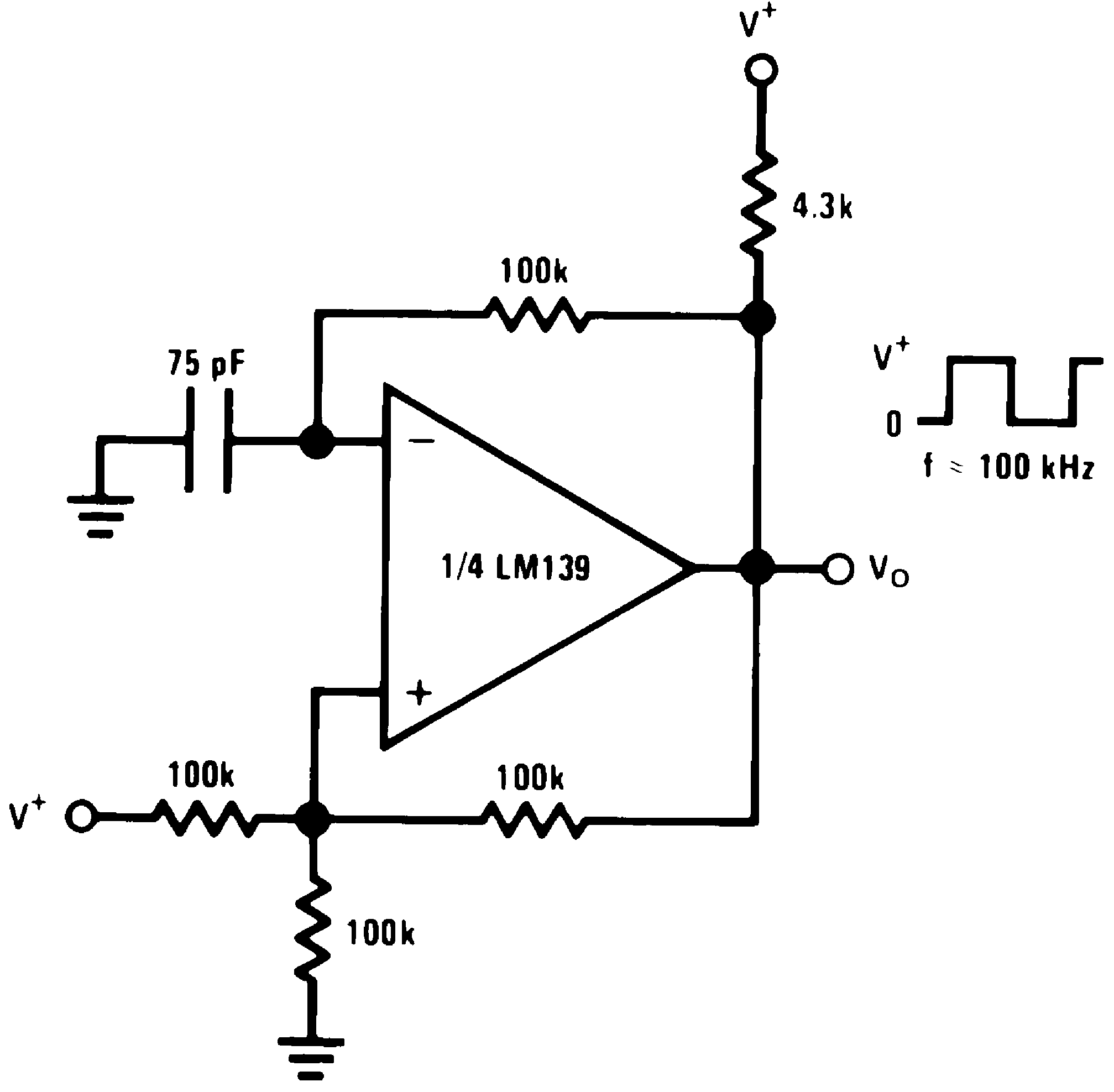 Figure 21. Squarewave Oscillator
Figure 21. Squarewave Oscillator(V+= 15 VDC)
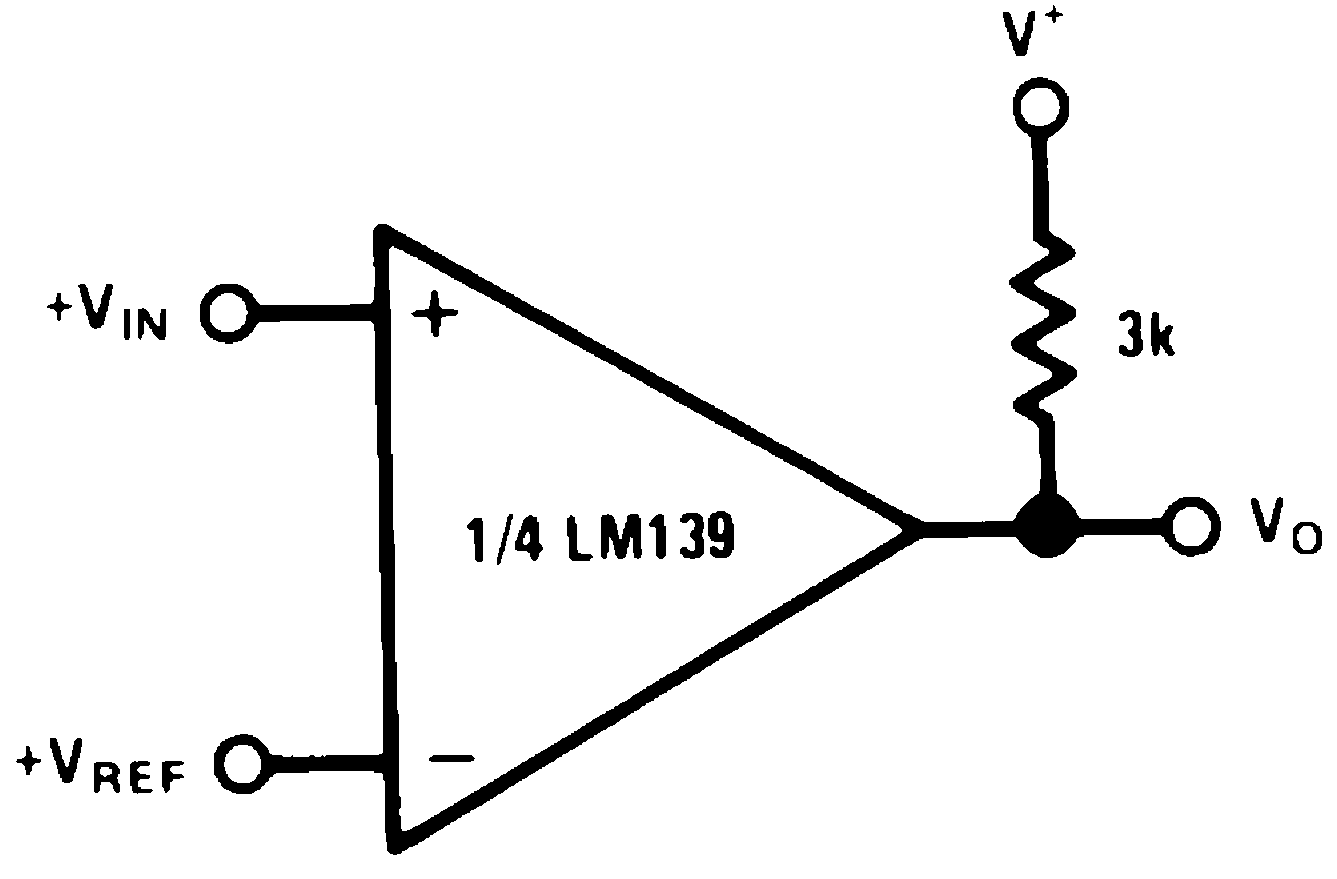 Figure 22. Basic Comparator
Figure 22. Basic Comparator(V+= 15 VDC)
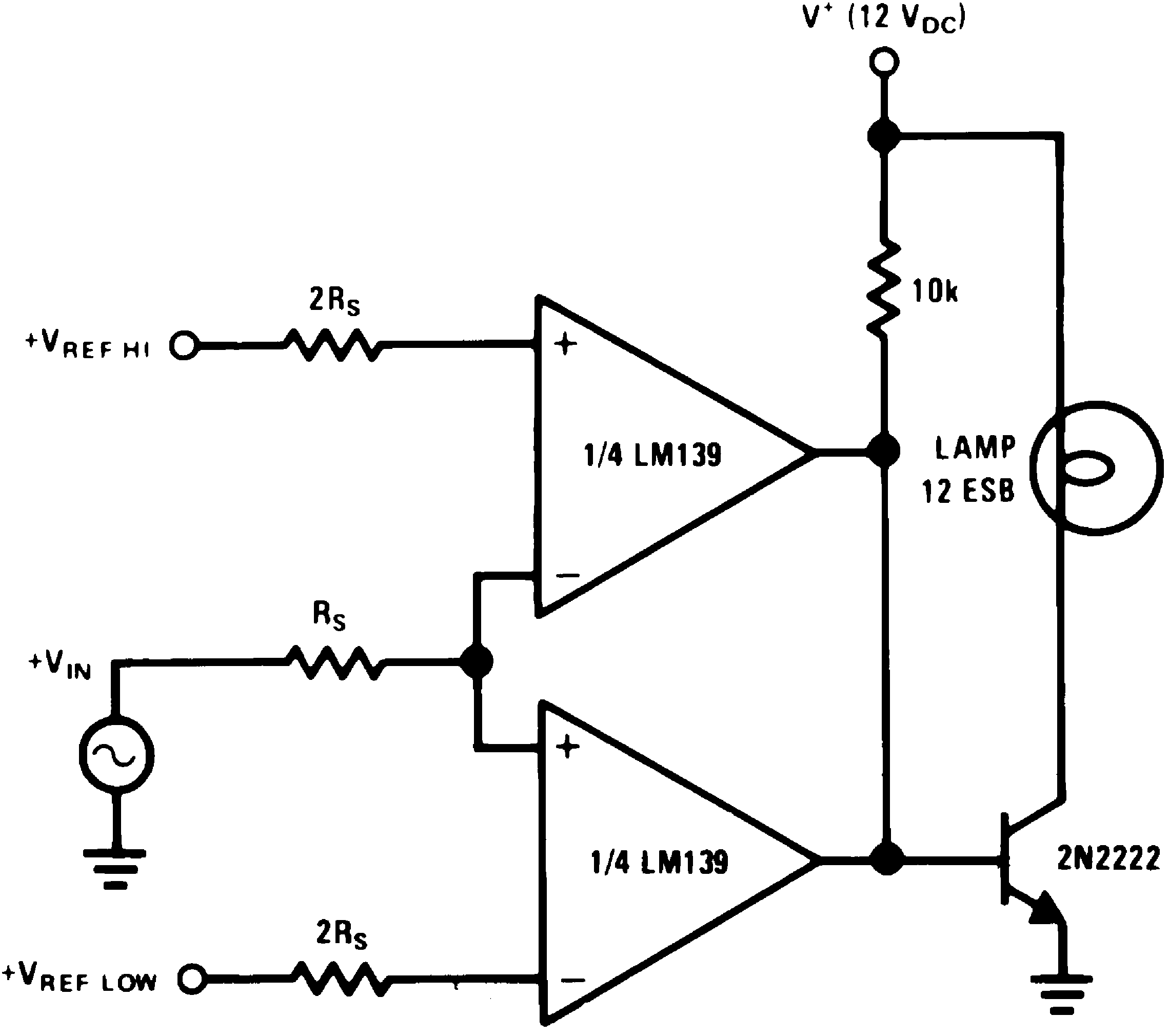 Figure 23. Limit Comparator
Figure 23. Limit Comparator(V+= 15 VDC)
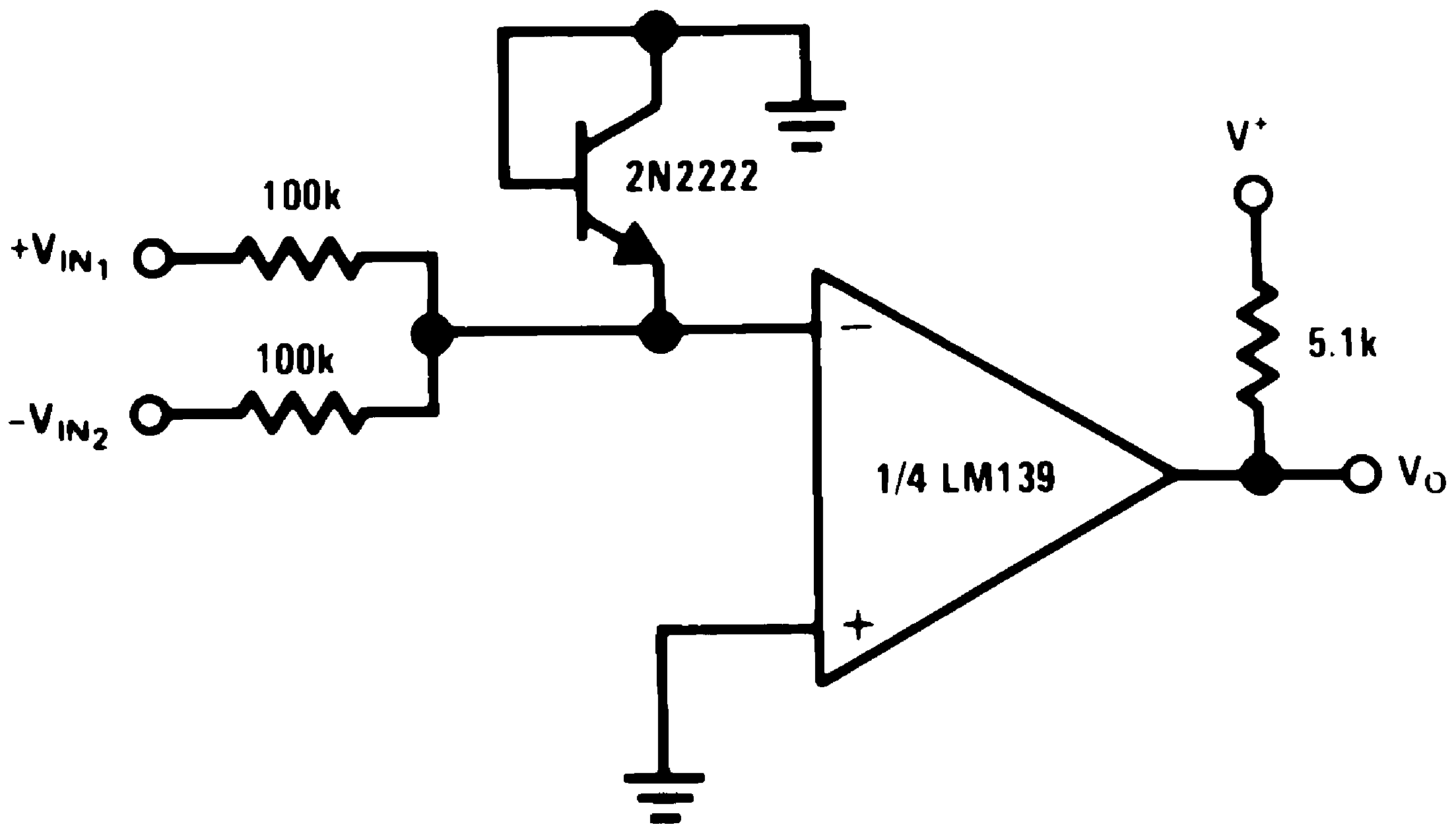 Figure 24. Comparing Input Voltages of Opposite Polarity
Figure 24. Comparing Input Voltages of Opposite Polarity(V+= 15 VDC)
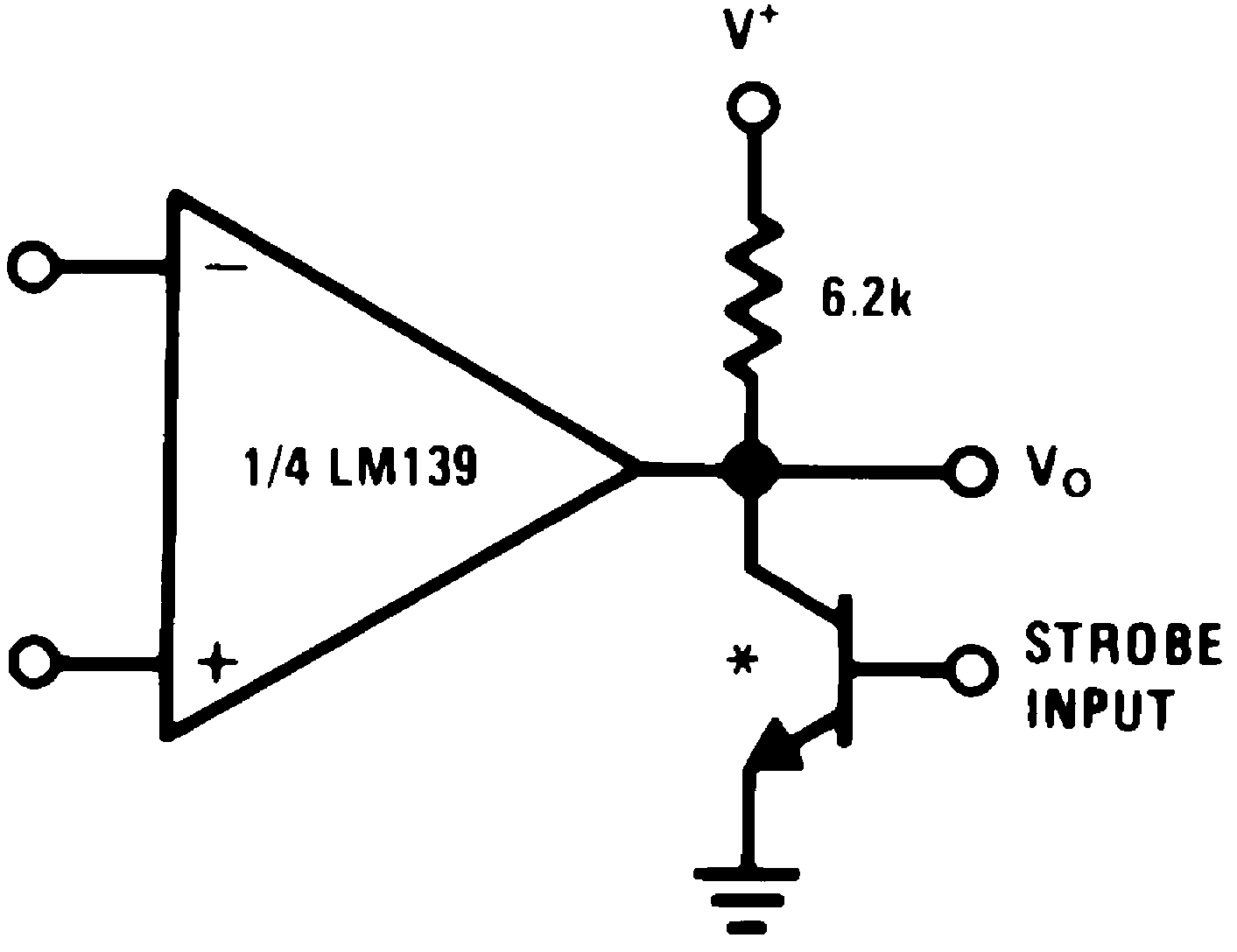
| * Or open-collector logic gate without pullup resistor |
(V+= 15 VDC)
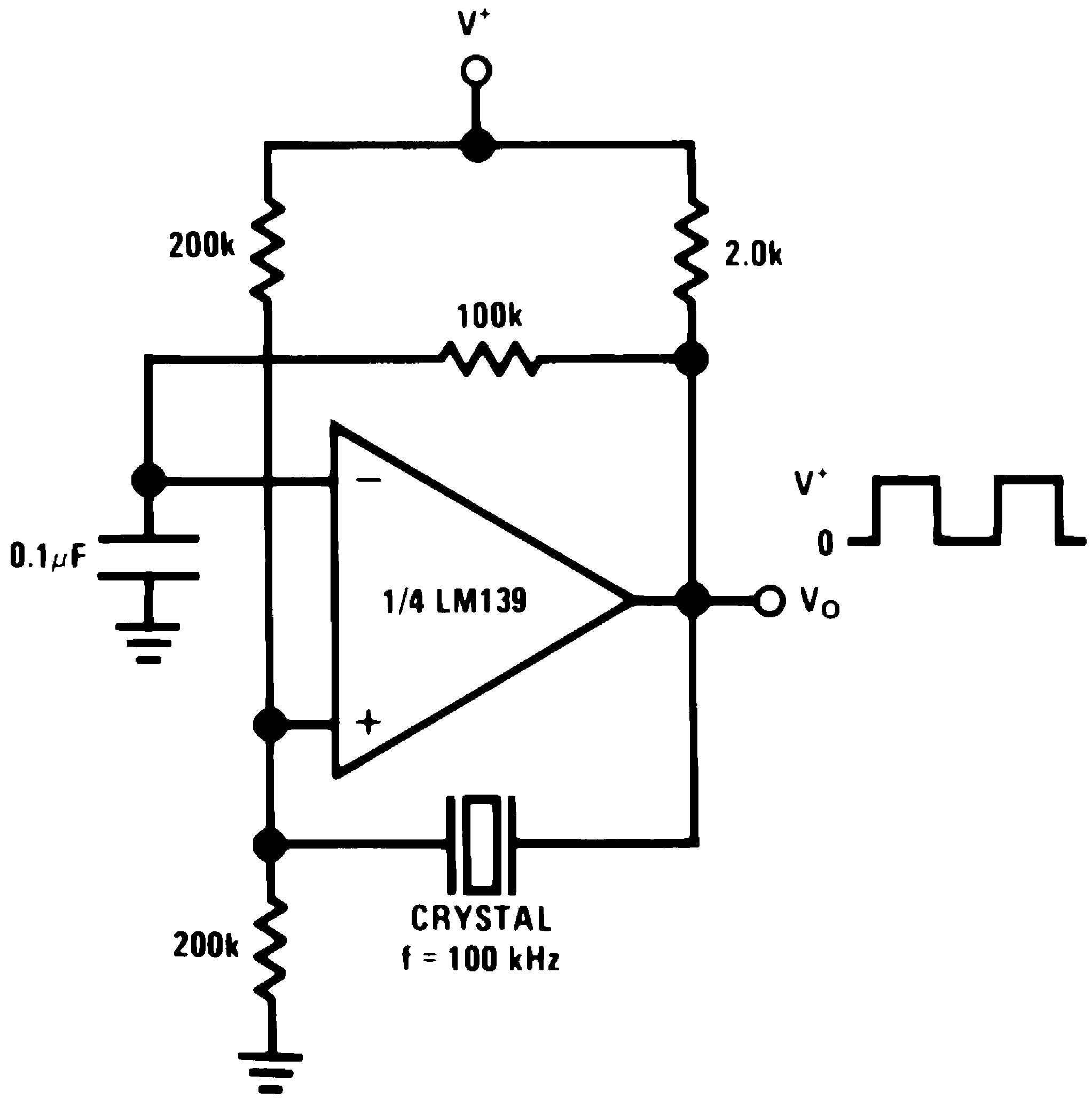 Figure 26. Crystal Controlled Oscillator
Figure 26. Crystal Controlled Oscillator(V+= 15 VDC)
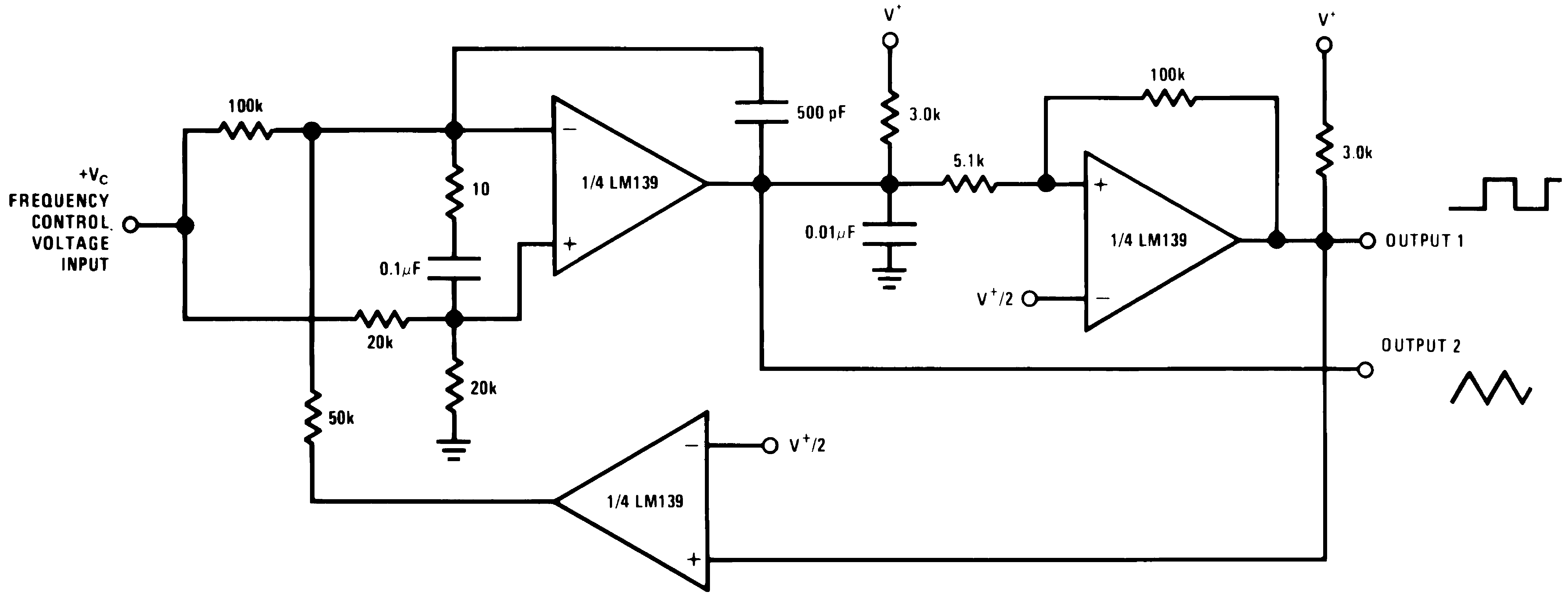
| 250 mVDC ≤ VC ≤ +50 VDC | ||
| 700 Hz ≤ fO ≤ 100 kHz |
V+ = +30 VDC
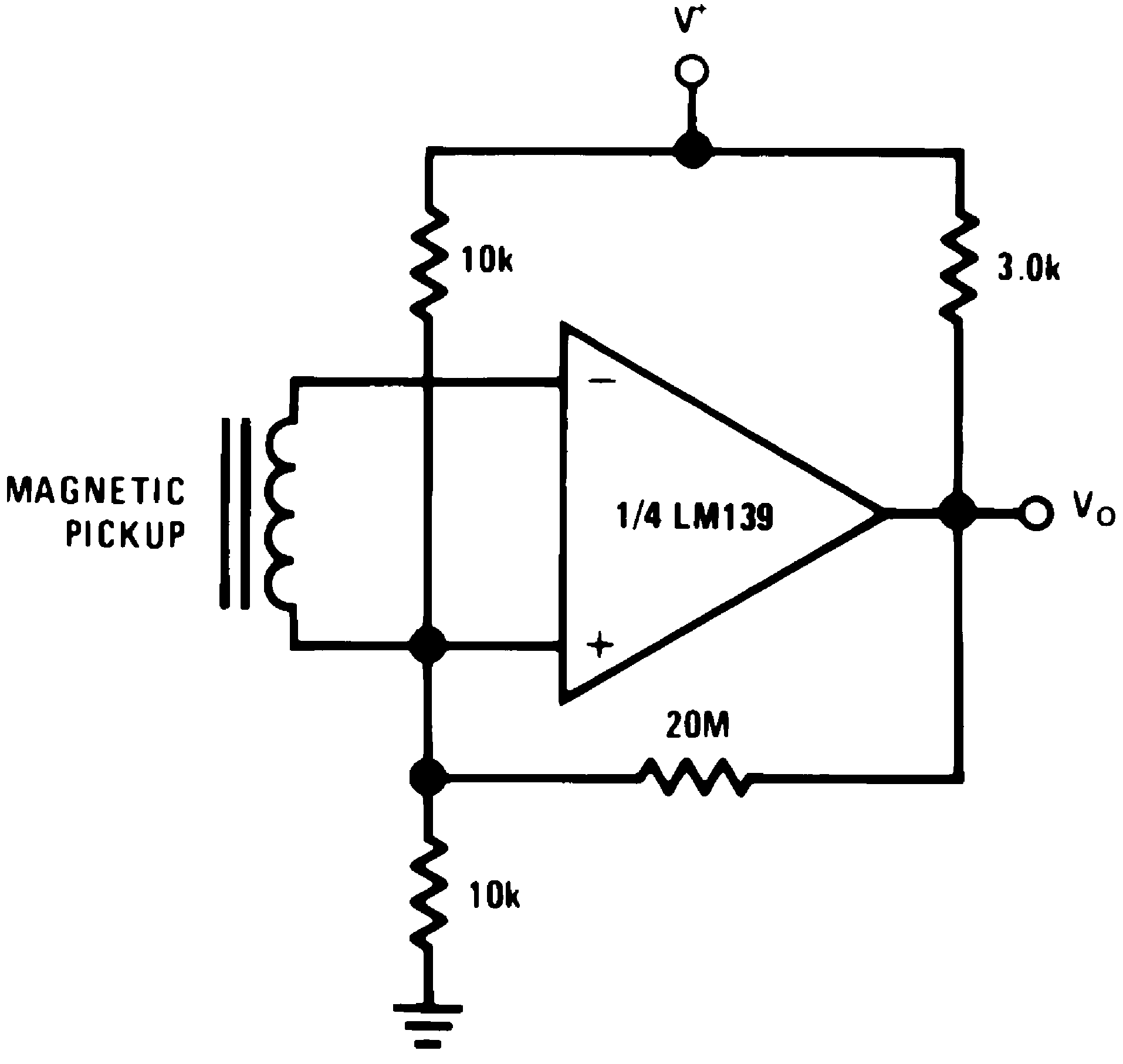 Figure 28. Transducer Amplifier
Figure 28. Transducer Amplifier(V+= 15 VDC)
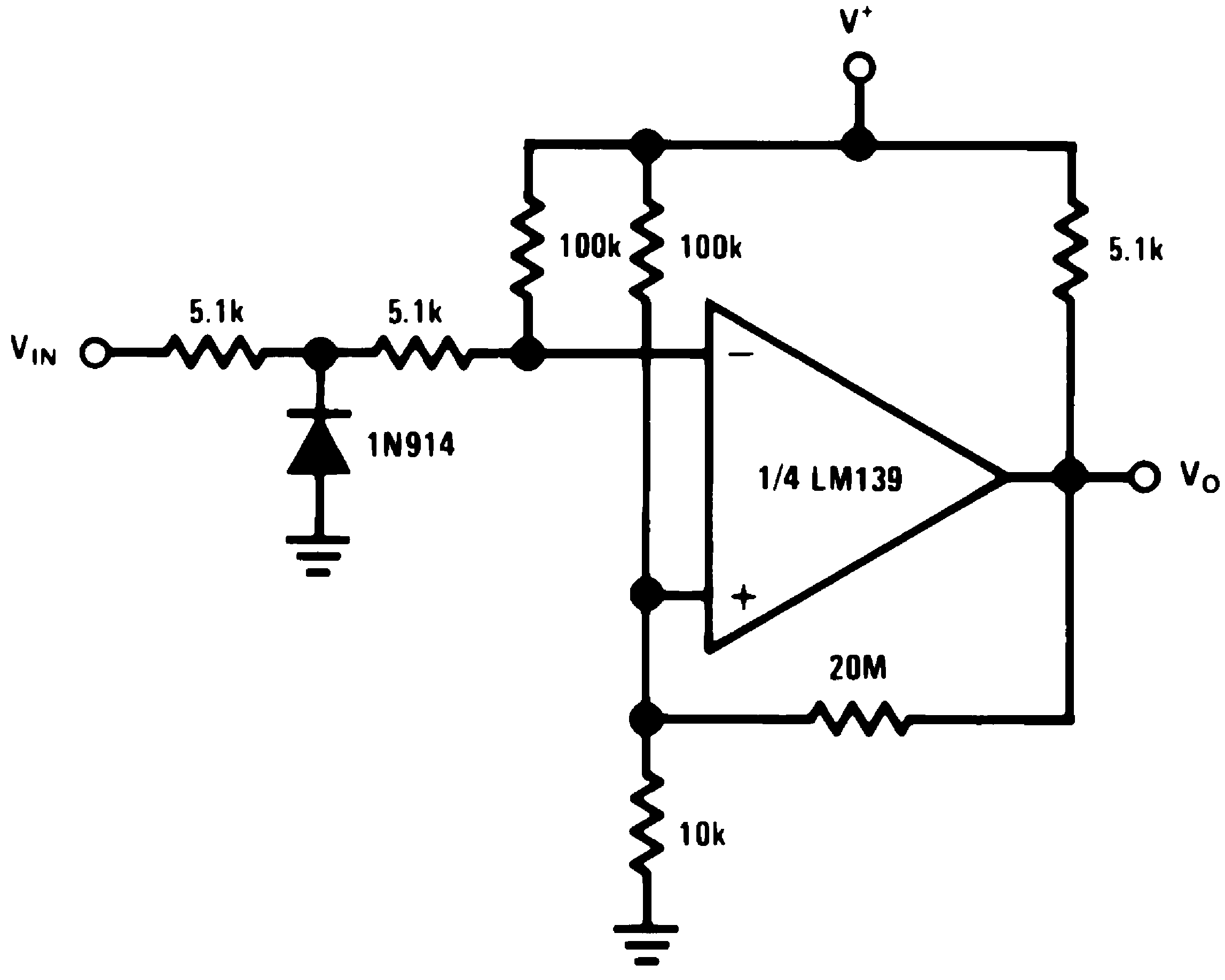 Figure 29. Zero Crossing Detector (Single Power Supply)
Figure 29. Zero Crossing Detector (Single Power Supply)(V+= 15 VDC)
8.3.1 Split-Supply Applications
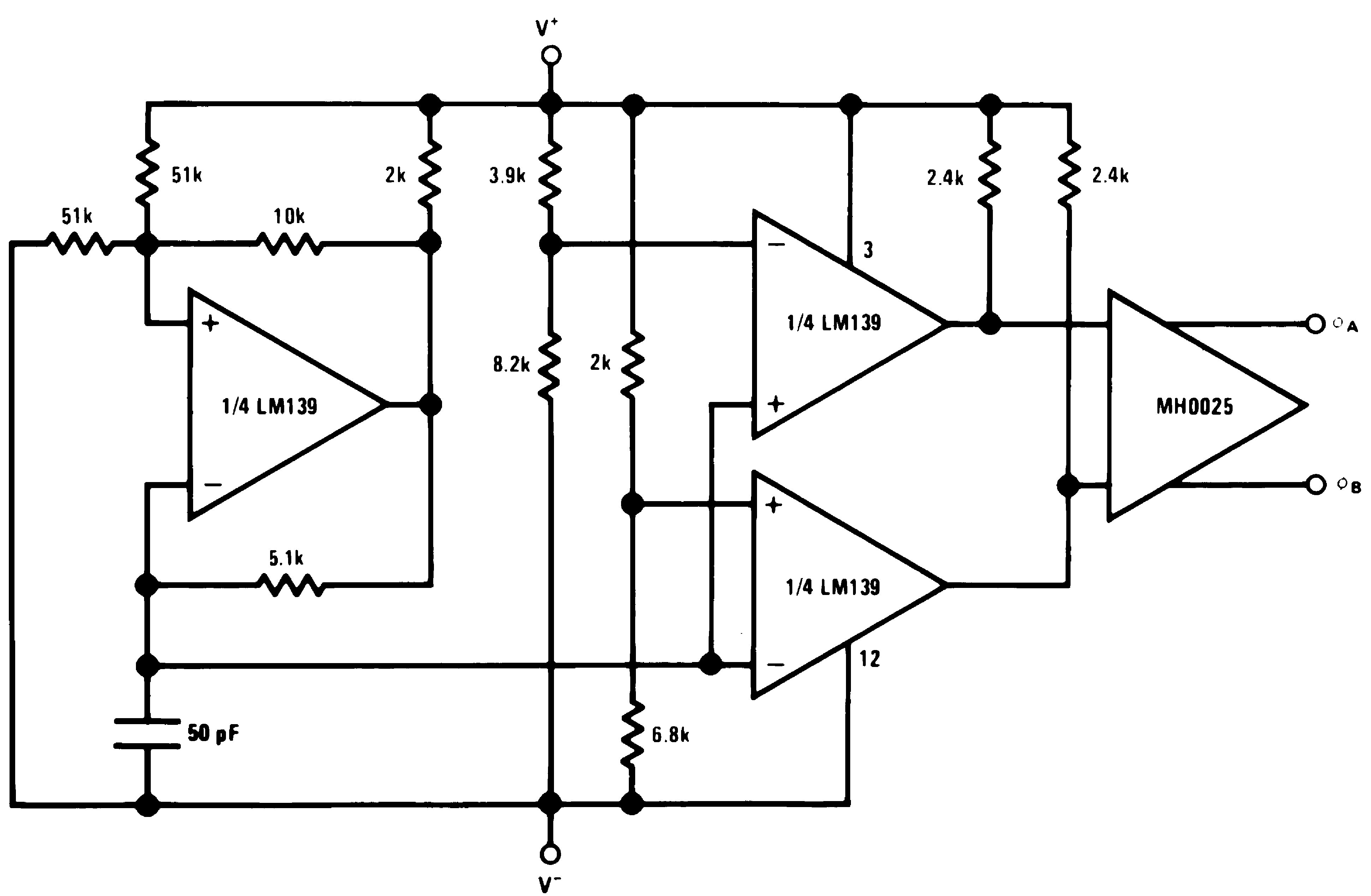 Figure 30. MOS Clock Driver
Figure 30. MOS Clock Driver(V+ = +15 VDC and V– = −15 VDC)
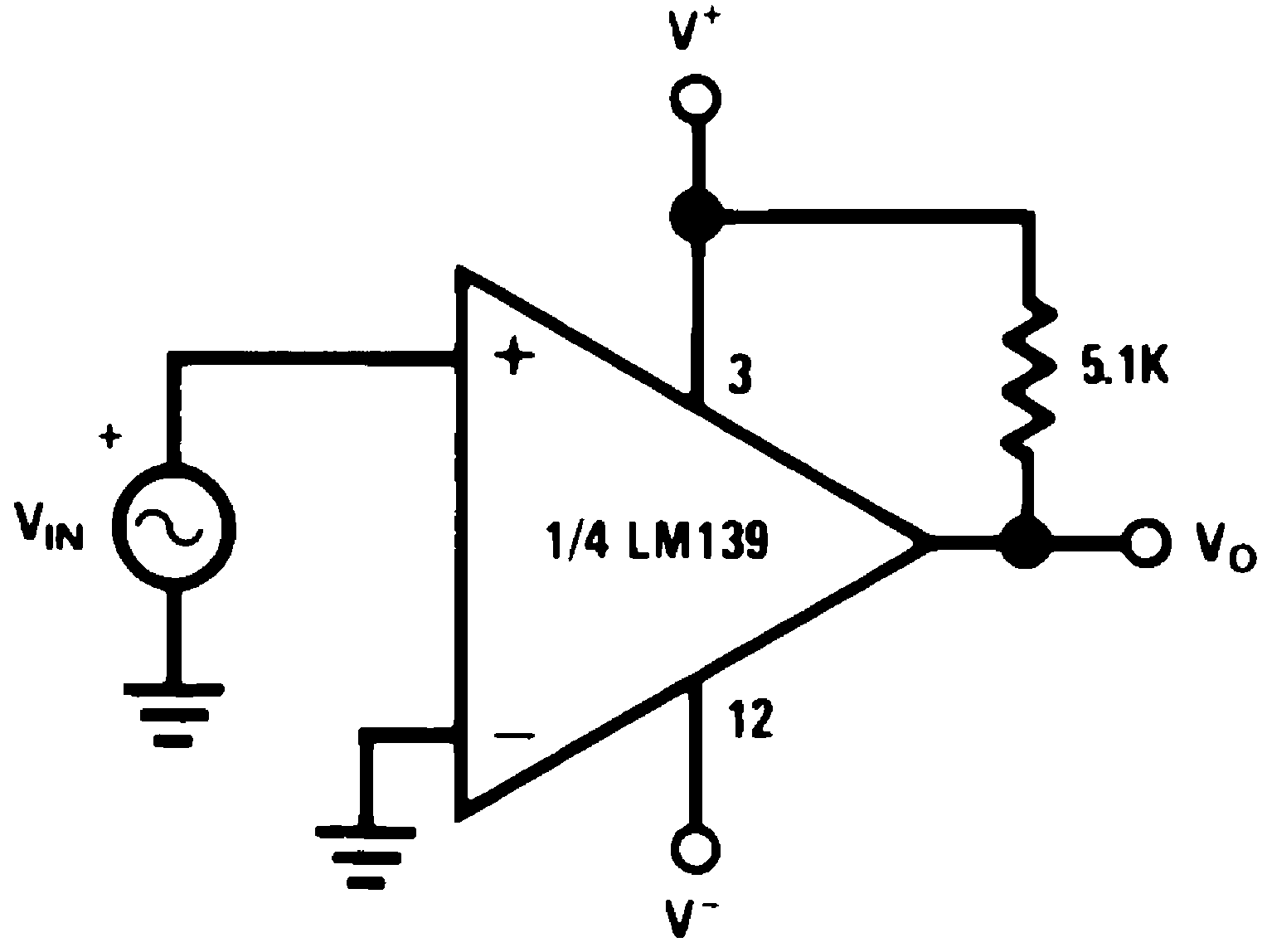
(V+ = +15 VDC and V– = −15 VDC)
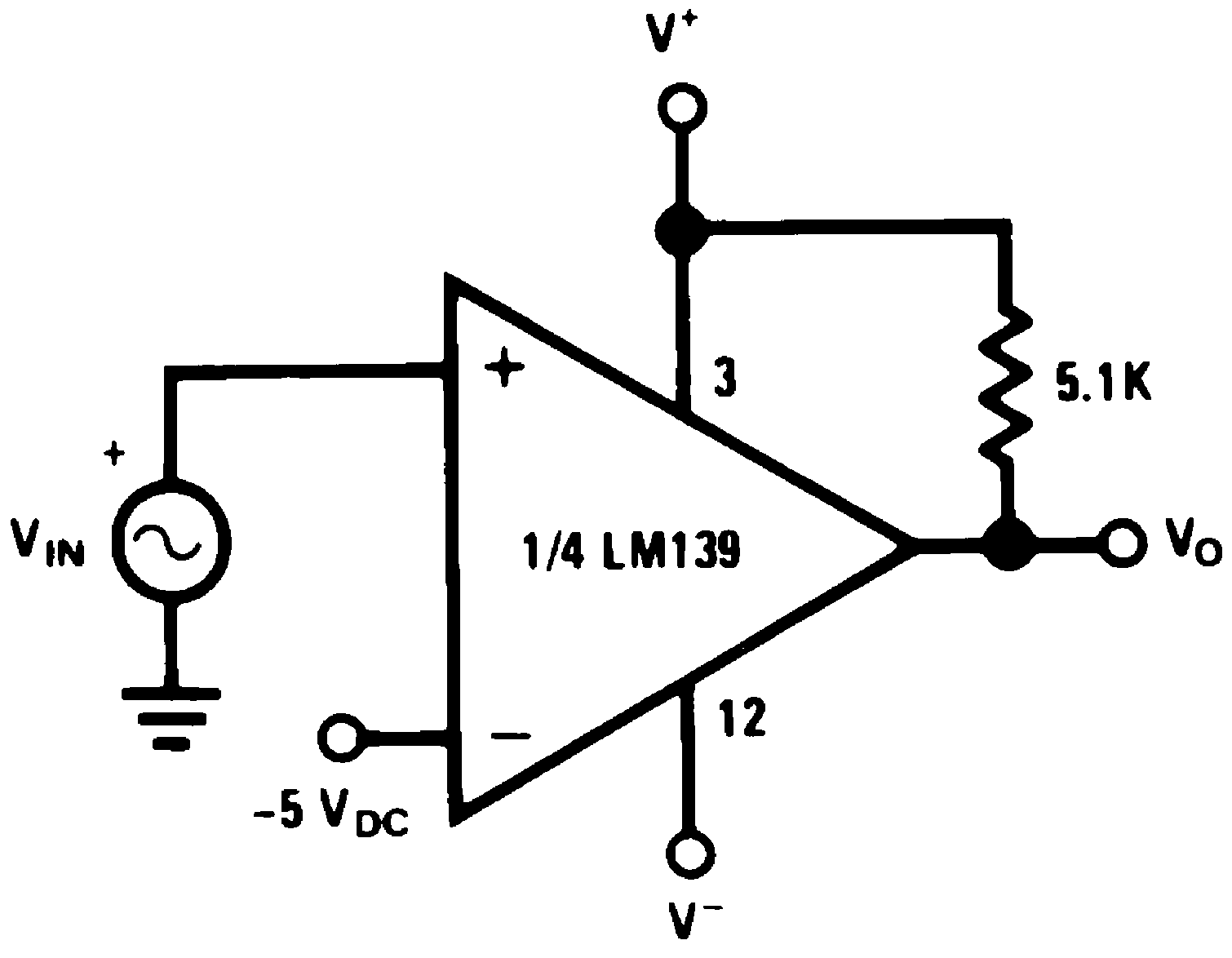
(V+ = +15 VDC and V– = −15 VDC)