ZHCSEG6F December 2015 – May 2025 TCAN330 , TCAN330G , TCAN332 , TCAN332G , TCAN334 , TCAN334G , TCAN337 , TCAN337G
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1特性
- 2應(yīng)用
- 3說明
- Device Options
- 4Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5Specifications
- Parameter Measurement Information
- 6Detailed Description
- 7Application Information Disclaimer
- Device and Documentation Support
- 8Revision History
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封裝選項
機械數(shù)據(jù) (封裝 | 引腳)
散熱焊盤機械數(shù)據(jù) (封裝 | 引腳)
- DCN|8
訂購信息
7.3.2 Differential Signal
CAN is a differential bus where complementary signals are sent over two wires and the voltage difference between the two wires defines the logical state of the bus. The differential CAN receiver monitors this voltage difference and outputs the bus state with a single ended logic level output signal.
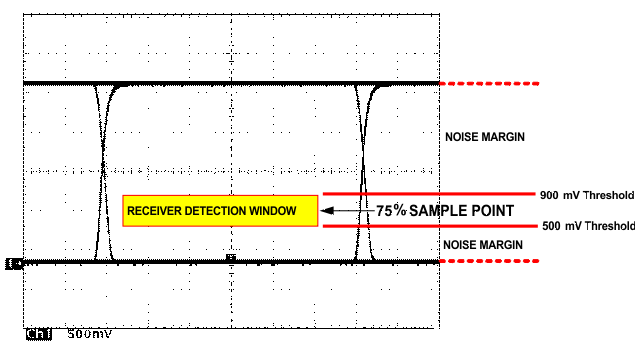 Figure 7-6 Typical Differential Output Waveform
Figure 7-6 Typical Differential Output WaveformThe CAN driver creates the differential voltage between CANH and CANL in the dominant state. The dominant differential output of the TCAN33x is greater than 1.5V and less than 3V across a 60Ω load as defined by the ISO11898 standard. These are the same limiting values for 5V supplied CAN transceivers. The bus termination resistors drive the recessive bus state and not the CAN driver.
A CAN receiver is required to output a recessive state when less than 500 mV of differential voltage exists on the bus, and a dominant state when more than 900mV of differential voltage exists on the bus. The CAN receiver must do this with common-mode input voltages from –2V to 7V. The TCAN33x family receivers meet these same input specifications as 5V supplied receivers.